Hormone Increase After Ovulation
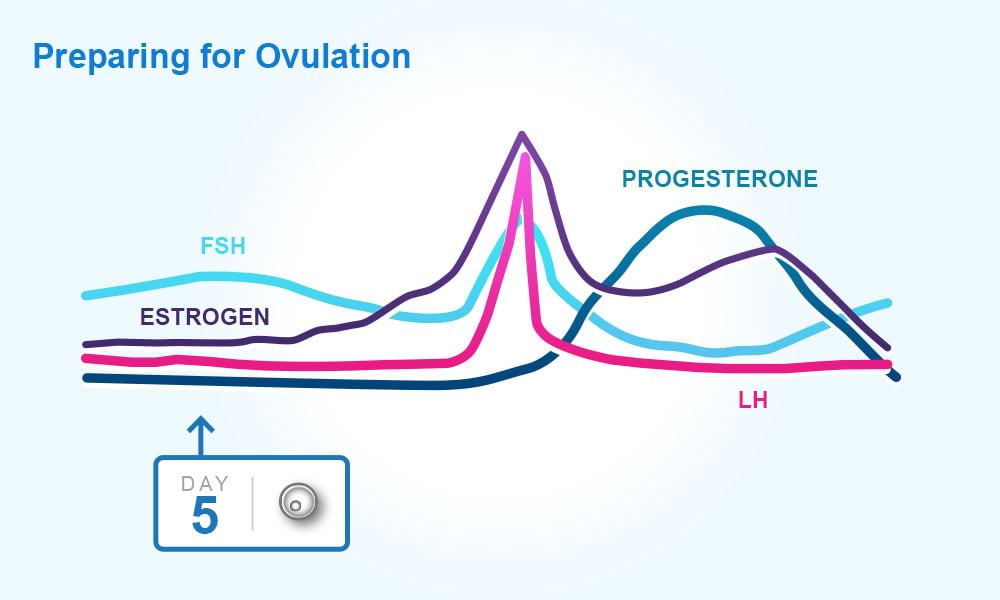
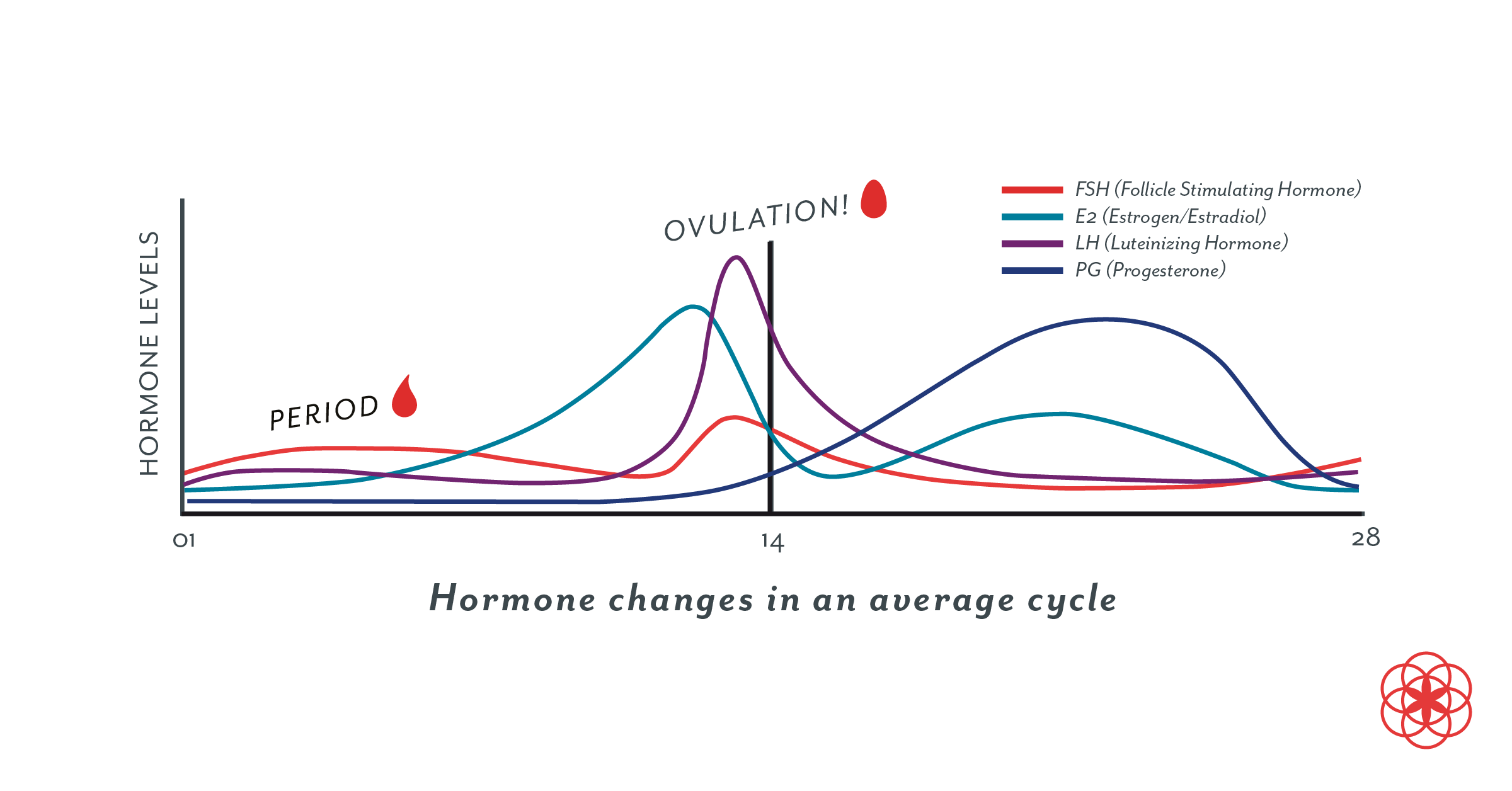
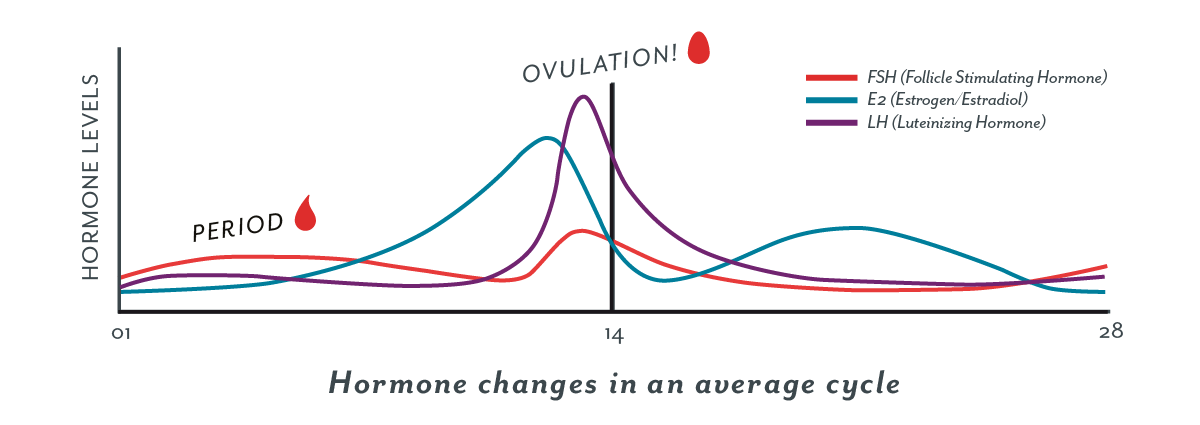
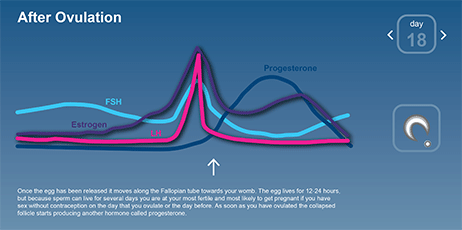
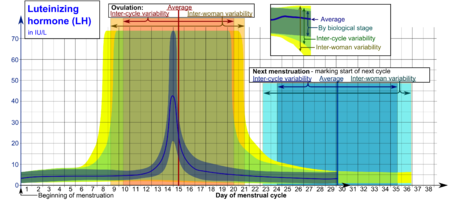
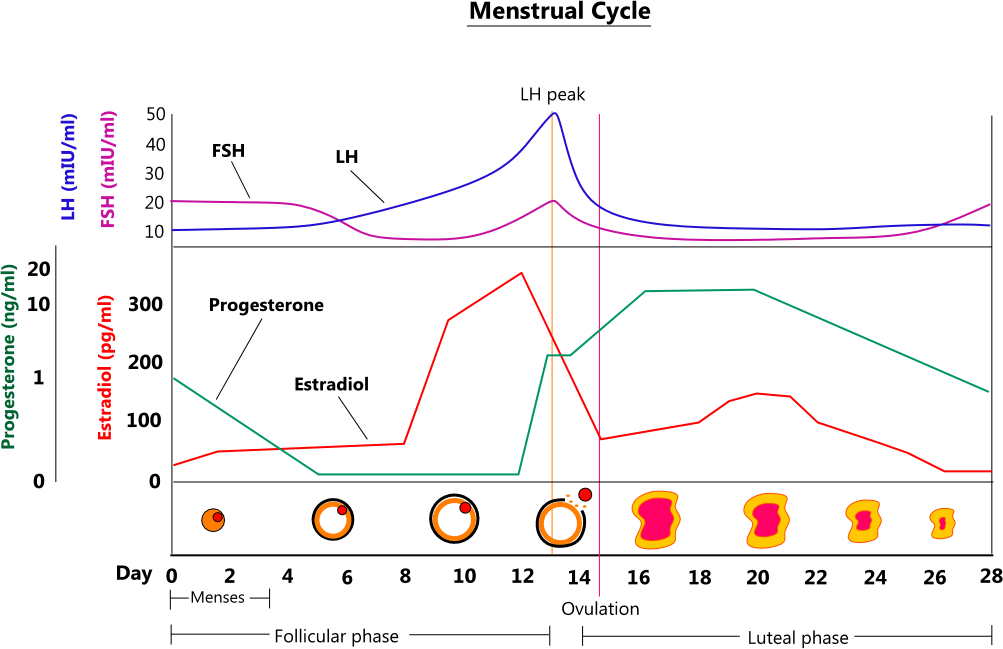
This hormone surge is what triggers ovulation about 24 to 36 hours later.
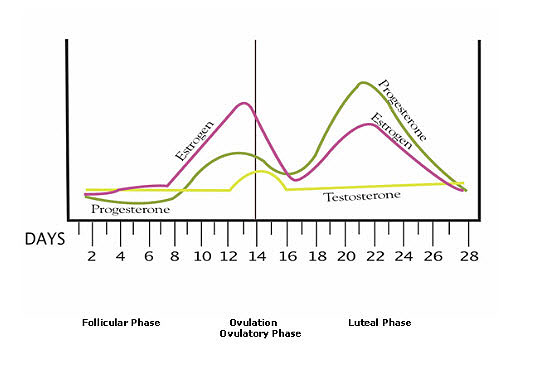
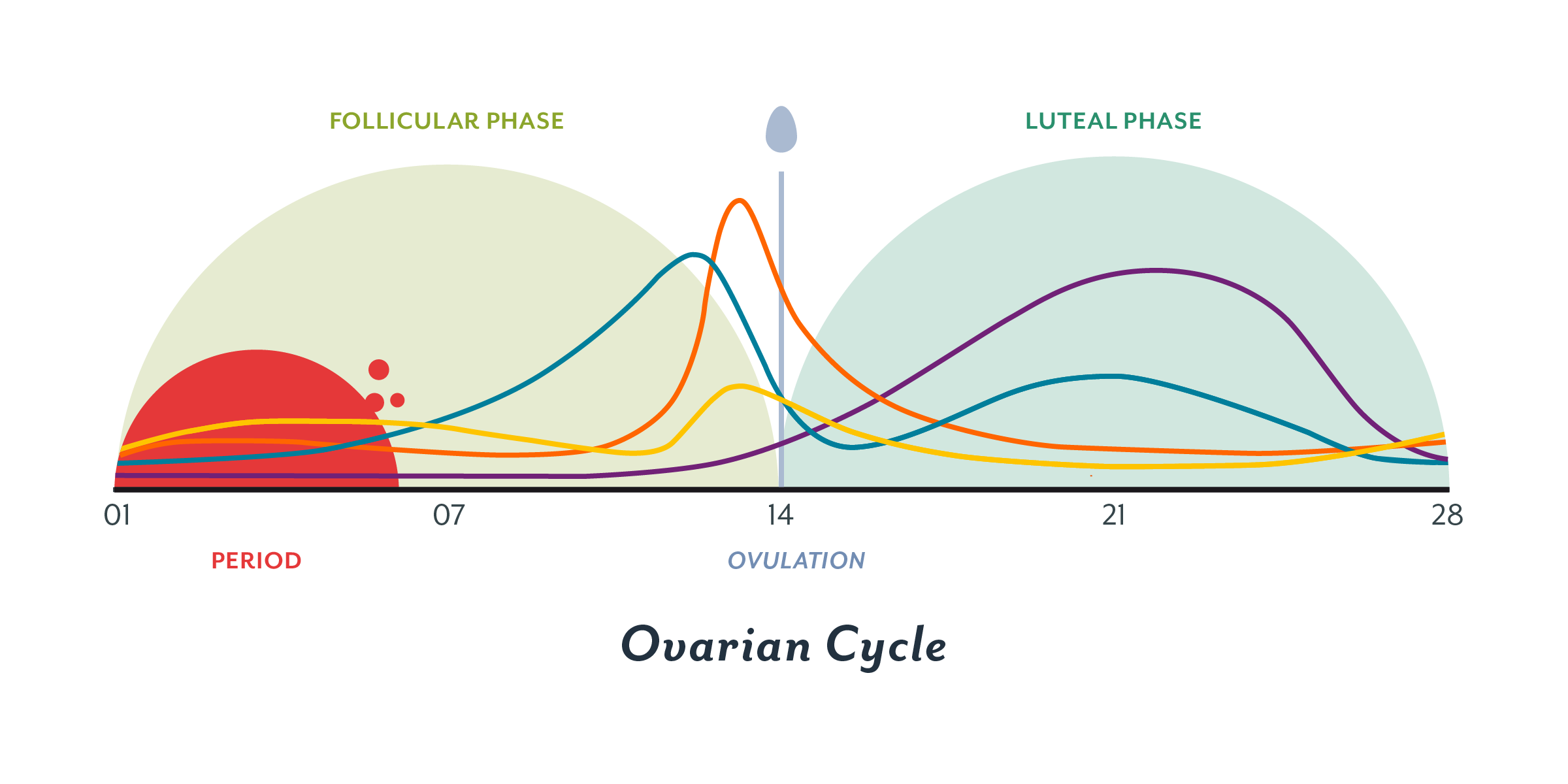
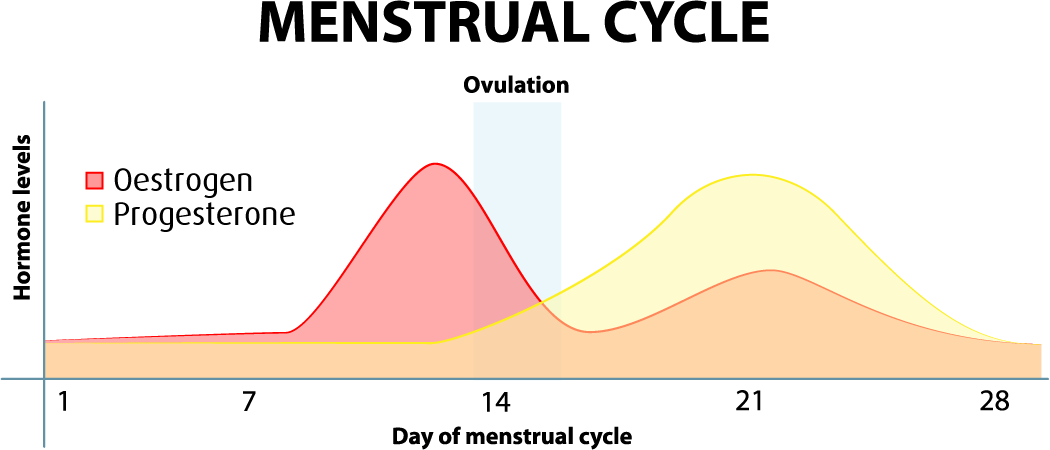
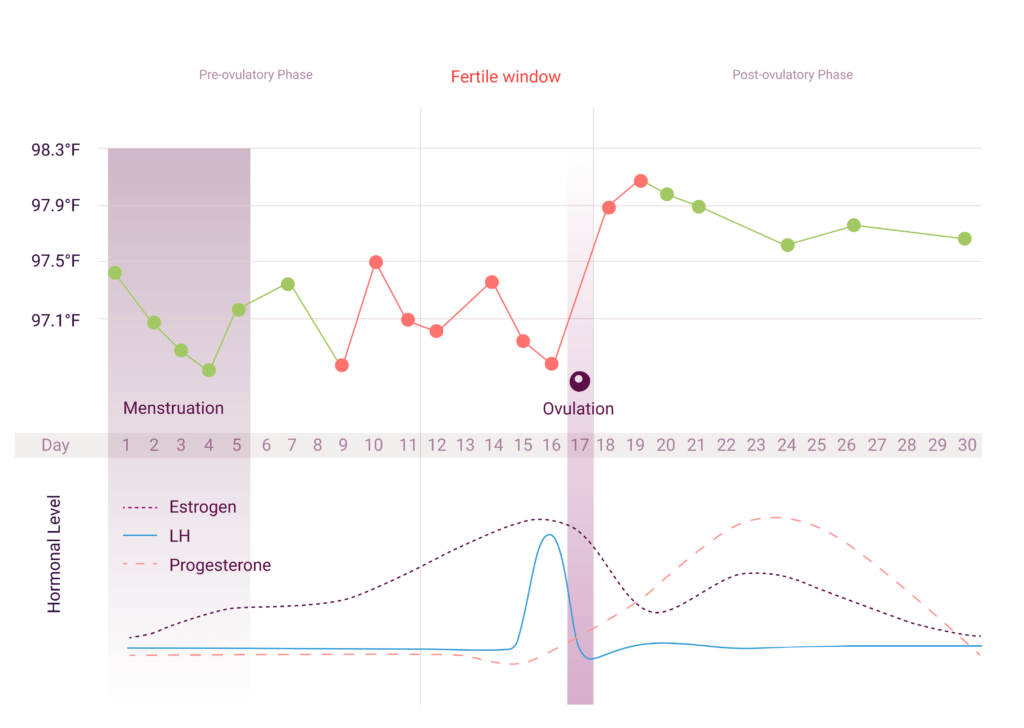
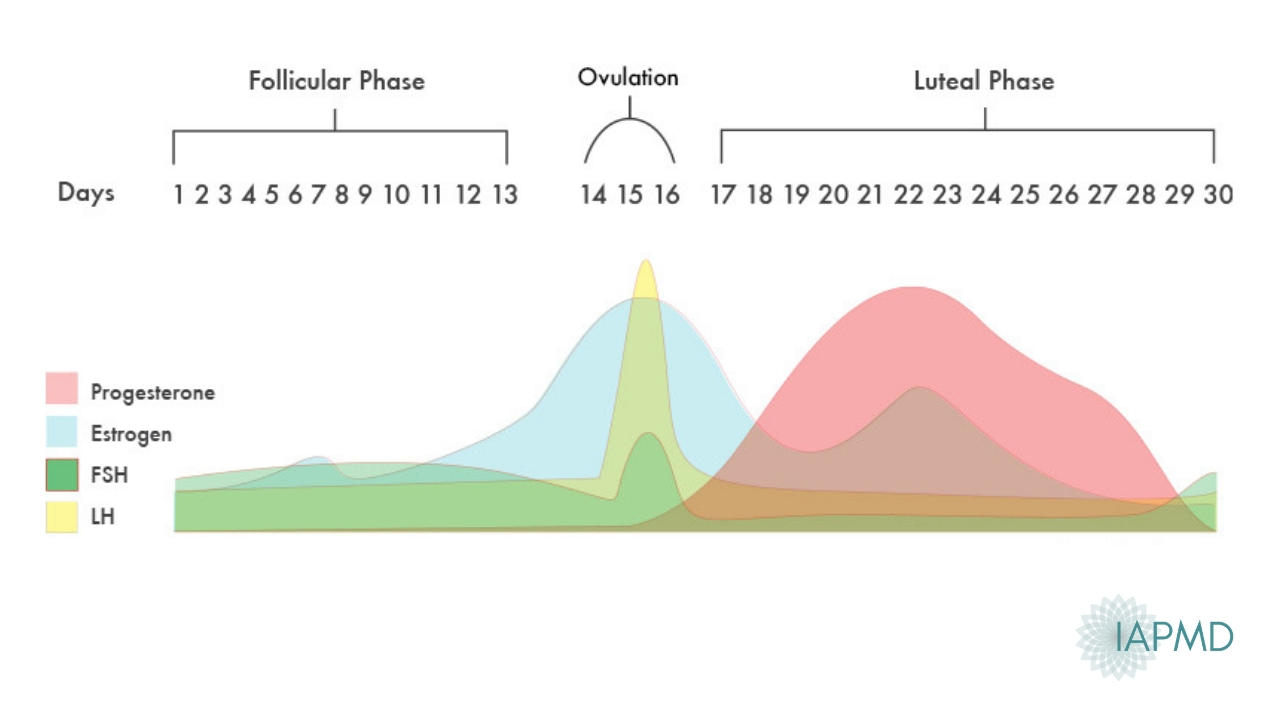
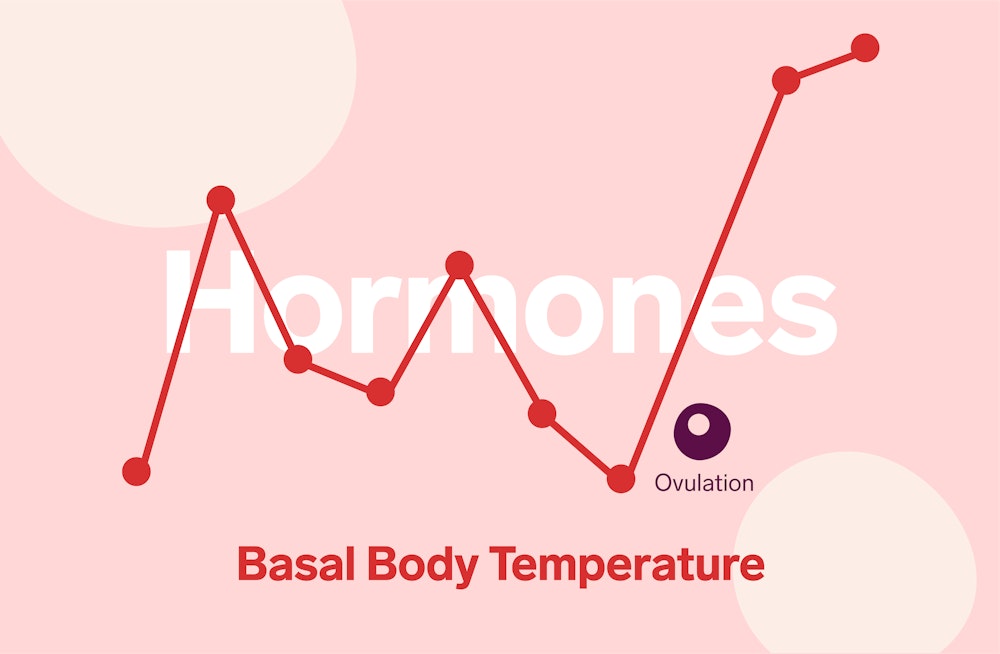
Hormone increase after ovulation. Lower e2 relative to the days before ovulation brings about changes in cervical mucus and progesterone leads to a detectable increase in basal body temperature. Called the lh surge this event causes one large dominant follicle to bulge from the surface of the ovary in preparation for ovulation. Estrogen is one of the most impactful hormones in the female body. Progesterone is the hormone that starts to increase after ovulation and remains high until your next period comes.
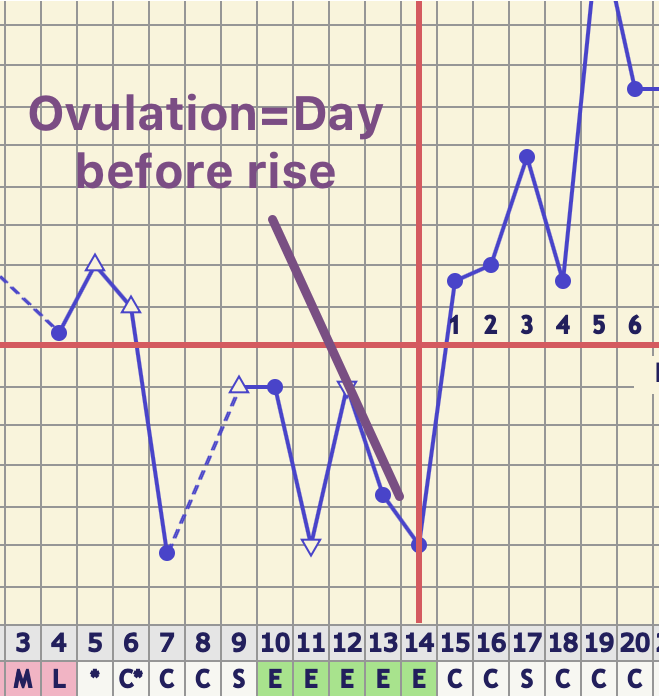
Ovulation refers to the release of an egg from one of the two ovaries. This is the phase where you can get pregnant. Just after this lh surge the most fertile period of the menstrual. High levels of estrogen and lh activate the complex biochemical interactions that lead to ovulation.
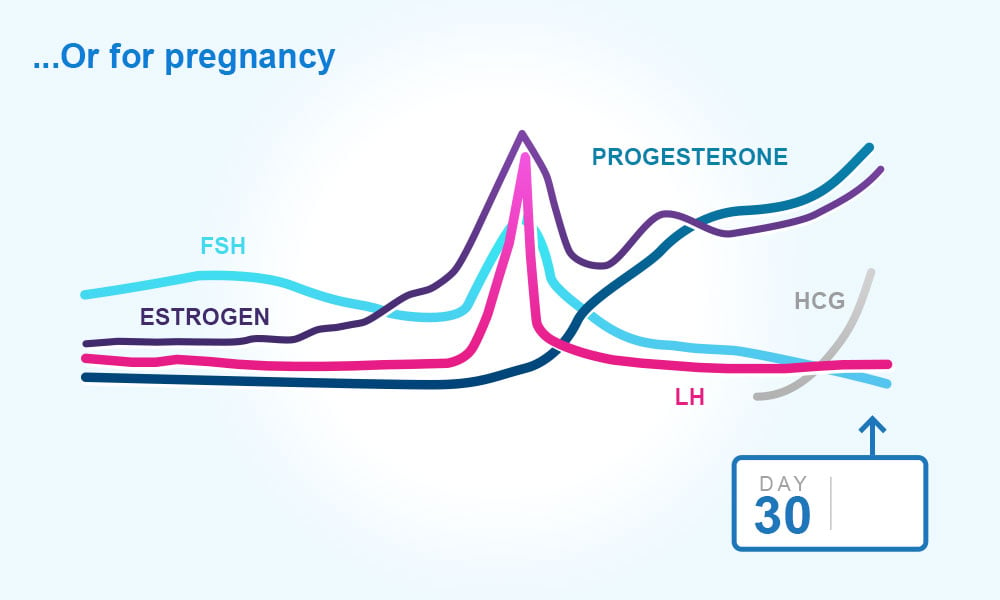
It signals the beginning of your fertile period. Ovulation is the release of a mature egg from the ovary. Hcg human chorionic gonadotropin is often called the pregnancy hormone because it is made by cells formed in the placenta which nourishes the egg after it has been fertilized and becomes attached to the uterine wall. This could explain in part why some women experience reduced libido when taking birth control pills.
The levels of luteinizing hormone lh rise just before ovulation and the increase triggers the release of an egg from an ovary. As a woman s menstrual cycle approaches mid cycle usually the 13th or 14th day high estrogen levels in her blood stimulate a sudden and large increase in the pituitary s output of lh. There are two main hormone driven physiological changes you might notice after ovulation. Estrogen is responsible for the stimulation of secondary female characteristics.
Maturing follicles produce estrogen which causes the luteinizing hormone to increase. Levels can first be detected by a blood test about 11 days after conception and about 12 14 days after conception by a urine test. Corpus luteum is left over in the fallopian tube. After ovulation the egg moves down the fallopian tube on the way to the uterus.
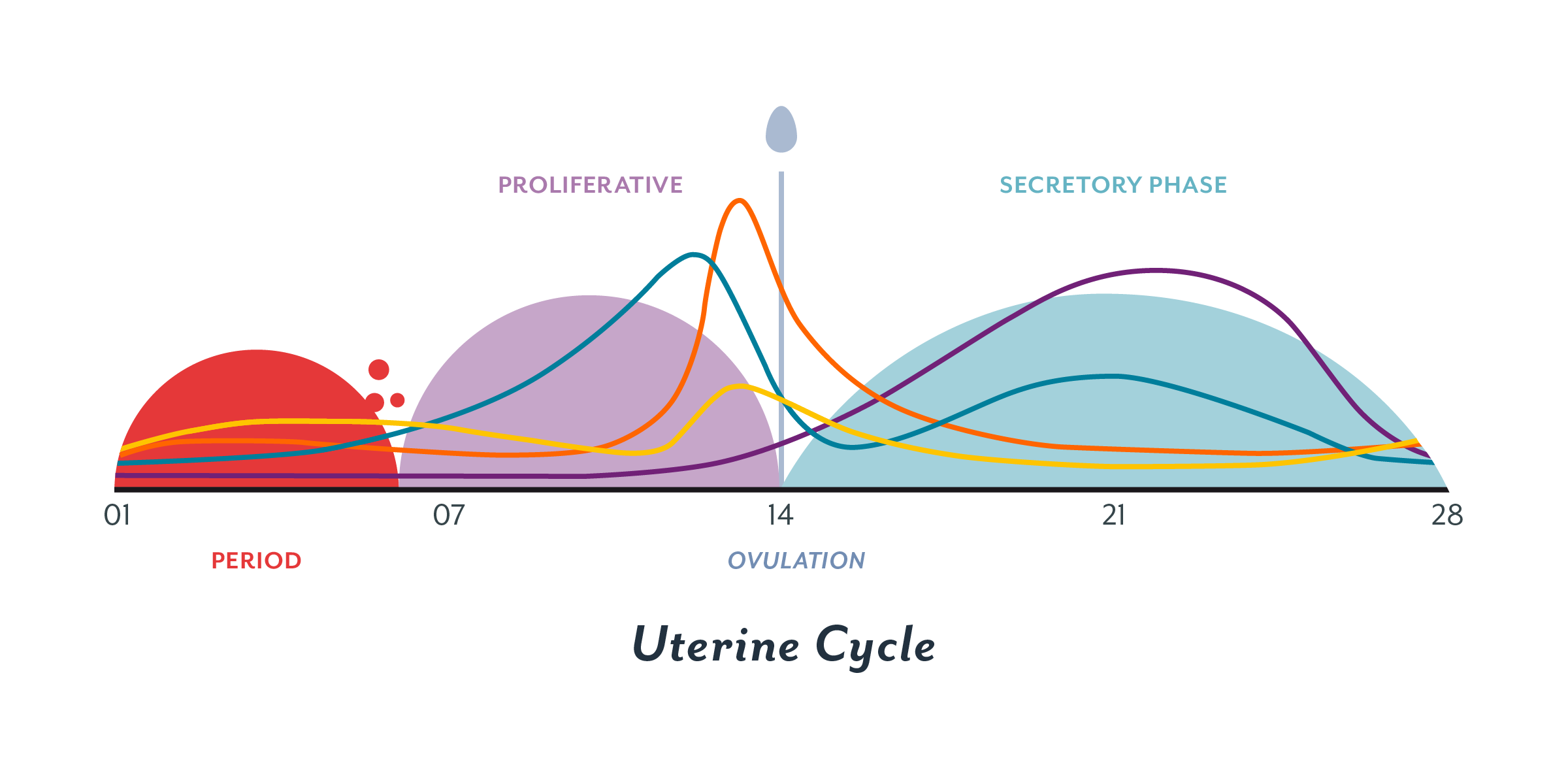
These thick walls are perfect for implantation of a fertilized egg.