How To Increase Progesterone After Ovulation

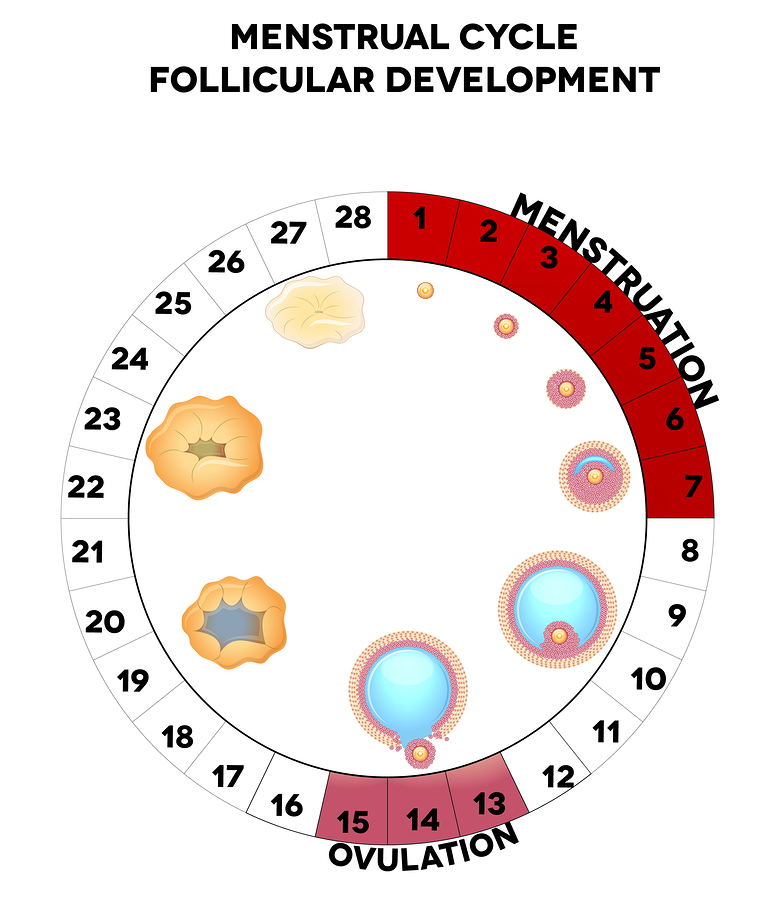
Progesterone is produced in the corpus luteum of the ovaries this is a temporary gland that s produced following the release of an egg from the ovary.
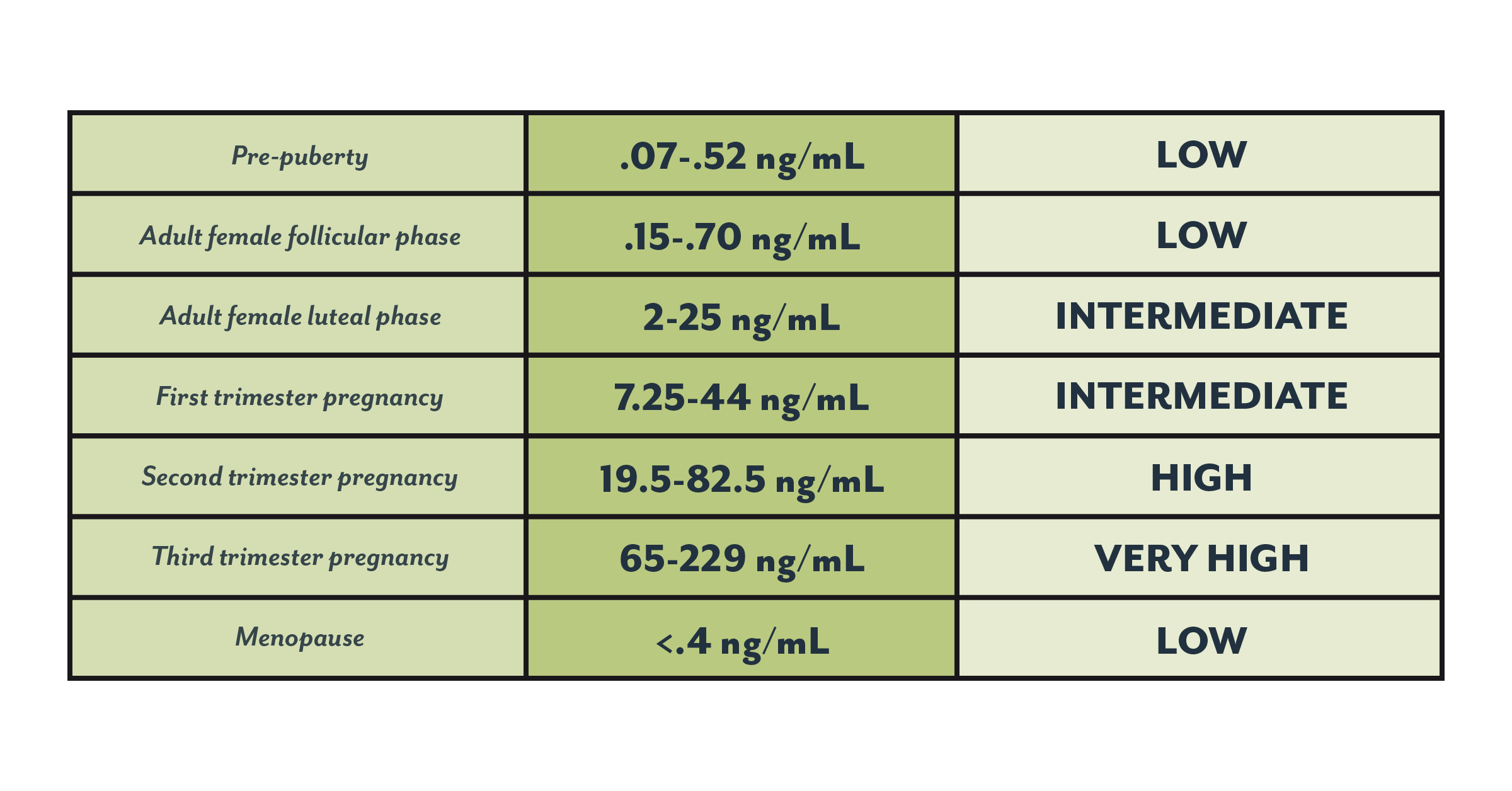
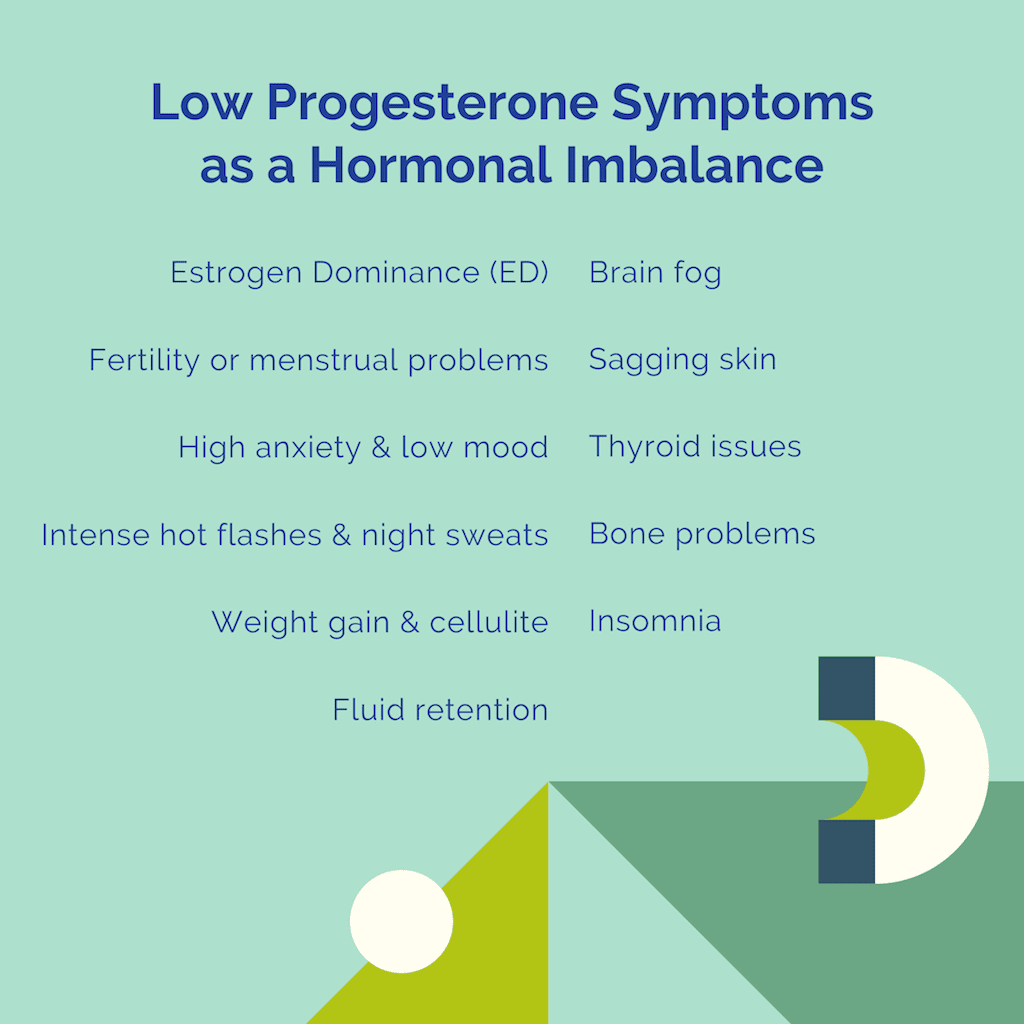
How to increase progesterone after ovulation. Serum progesterone is low during the follicular phase with levels being less than 1 5 ng ml. After menopause serum progesterone of adrenal origin is under 0 5 ng ml. One of the main actions of progesterone with fertility is to help support a developing embryo. These thick walls are perfect for implantation of a fertilized egg.
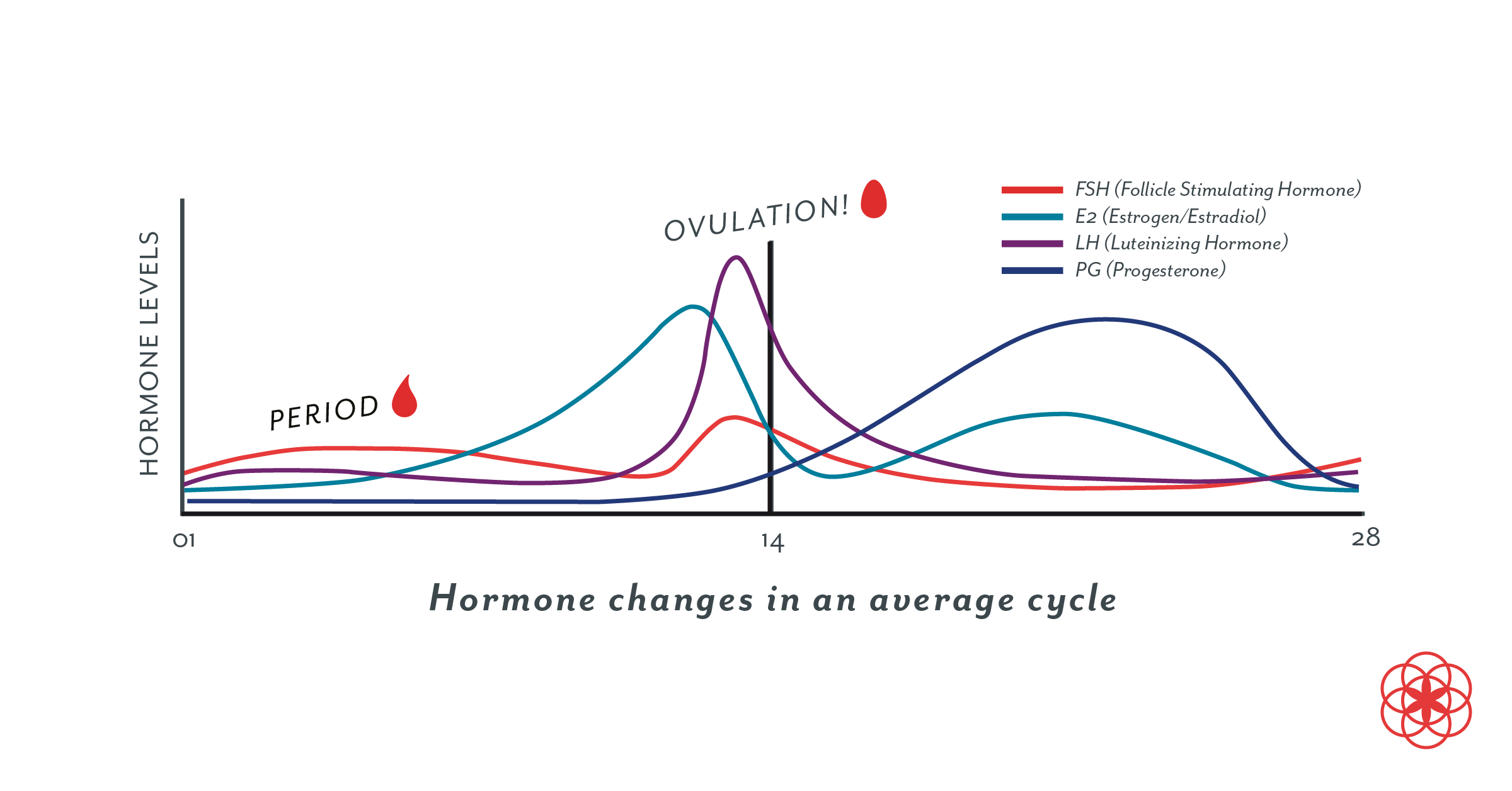
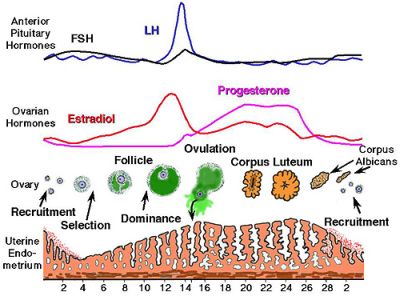
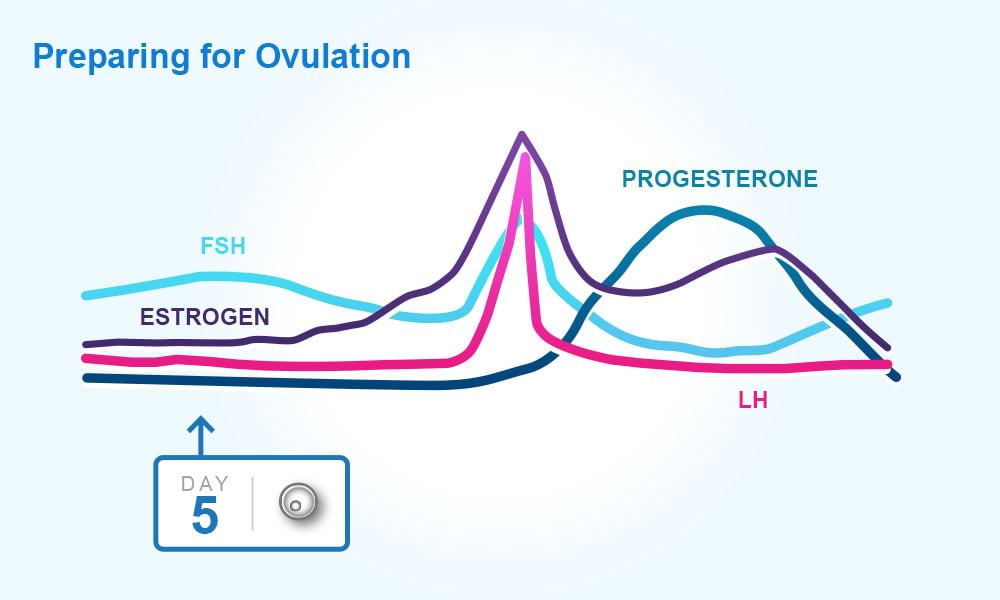
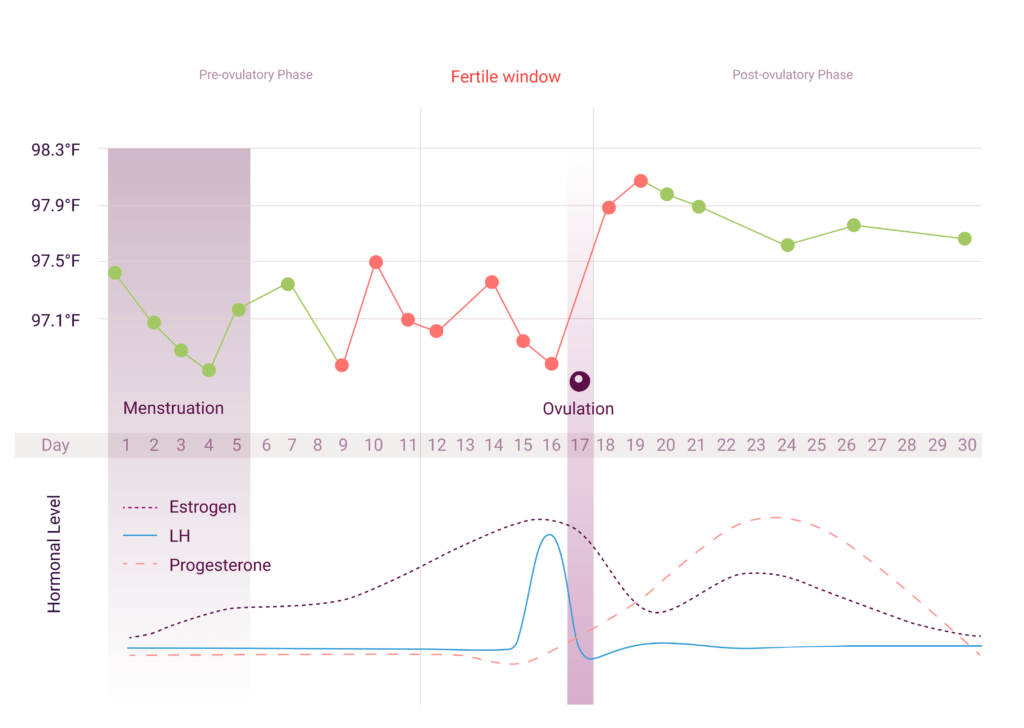
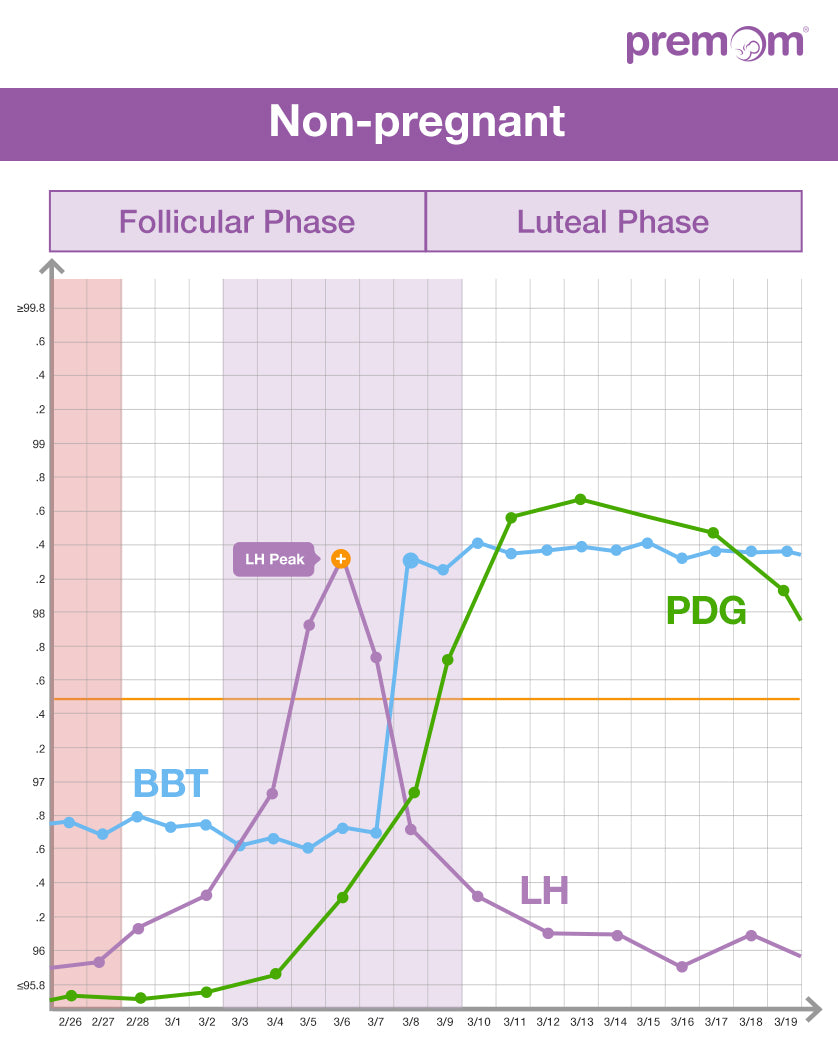
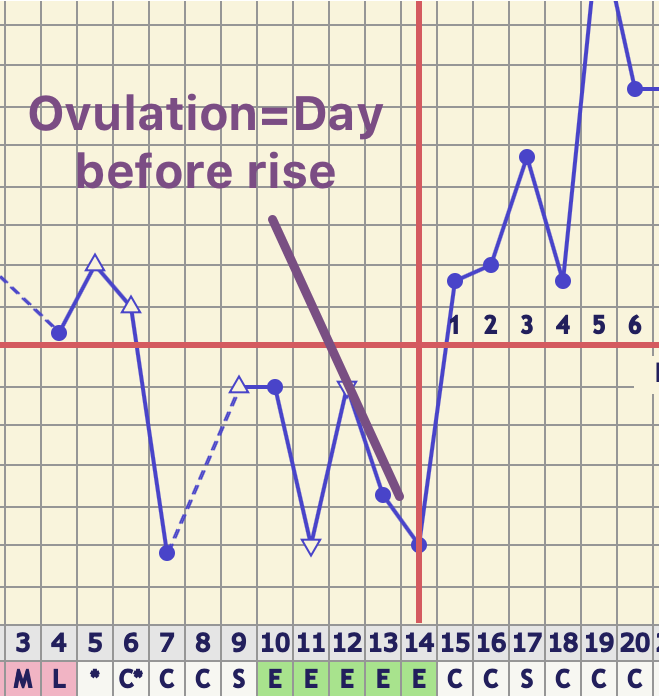
After ovulation progesterone production is triggered by luteinizing hormone lh which stimulates the corpus luteum the remnant egg sac in the ovary to produce progesterone. The adrenal glands and the placenta can. If pregnancy does not occur after ovulation progesterone levels drop and you will start to menstruate. Corpus luteum is left over in the fallopian tube.
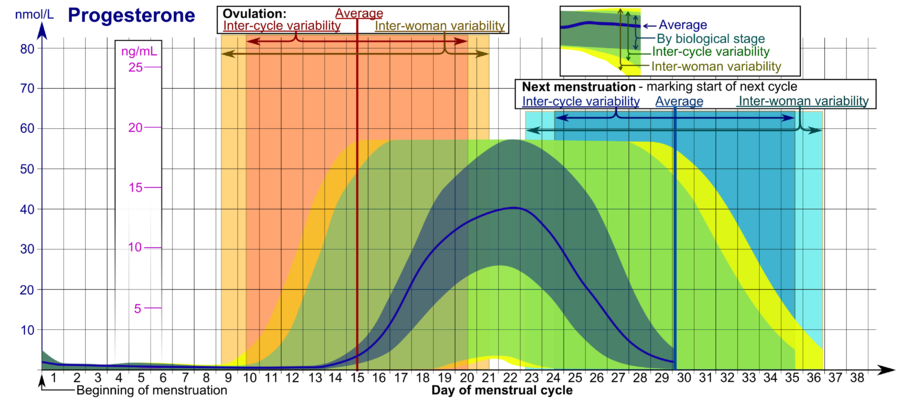
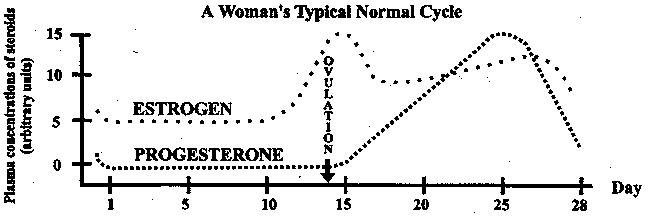
The corpus luteum signals a progesterone increase which leads to a thickening of uterine walls. Secreted from the ovary after ovulation progesterone is also the hormone that is responsible for staying pregnant. If you enjoy natural hormone balance then estrogen and progesterone work a little like yin and yang in your body. Levels begin to increase just before the onset of the lh surge and then increase progressively to peak 6 to 8 days after ovulation.
After ovulation the egg moves down the fallopian tube on the way to the uterus. After ovulation the corpus luteum is ready to release progesterone. Levels of this important hormone peak in the second half of a woman s cycle after ovulation the reason for progesterone s name which literally means promoting gestation. Progesterone is a steroid hormone initially secreted after ovulation by the corpus luteum an area in the ovary which develops after ovulation.
They increase right after ovulation and reach levels above 10 ng ml usually by 5 7 days after ovulation takes place. Progesterone is a female sex hormone that prepares the uterus for pregnancy. Progesterone is a hormone that is signals the lining of the uterus to get ready for implantation. Following ovulation this increase in progesterone helps further build the uterine lining during the endometrial secretory stage.
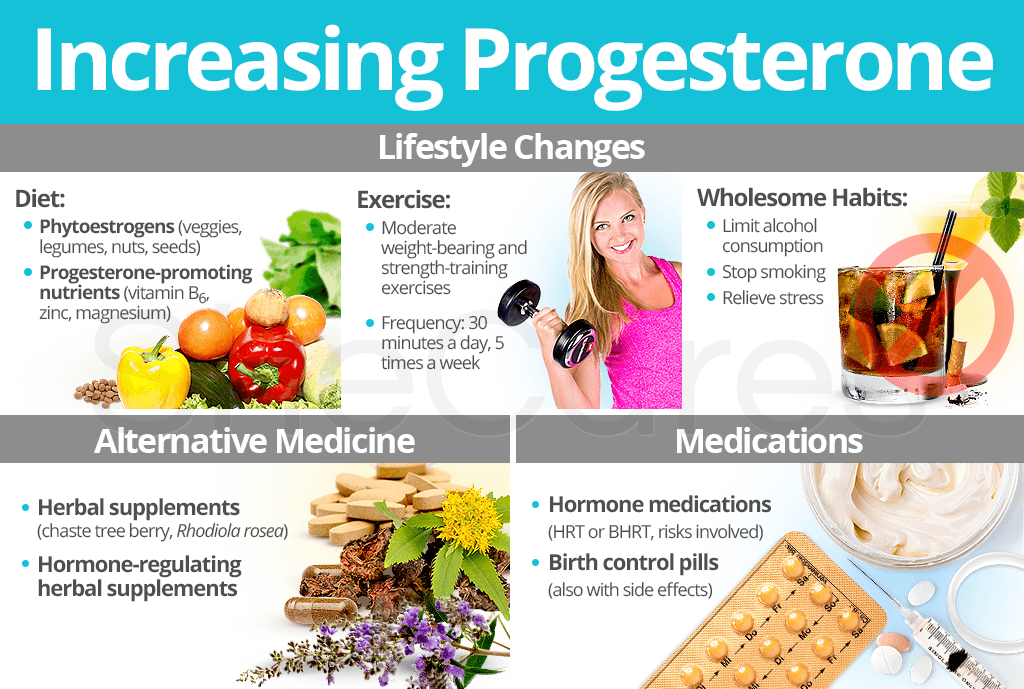
This is the time to support your progesterone levels so it can fulfill its roles to support and sustain a pregnancy. The reproductive function of this process is to prepare the uterus so that a fertilized egg can successfully implant bind to the mother s womb. Progesterone is the main hormone of the luteal phase which begins following ovulation around day 14 of your cycle.