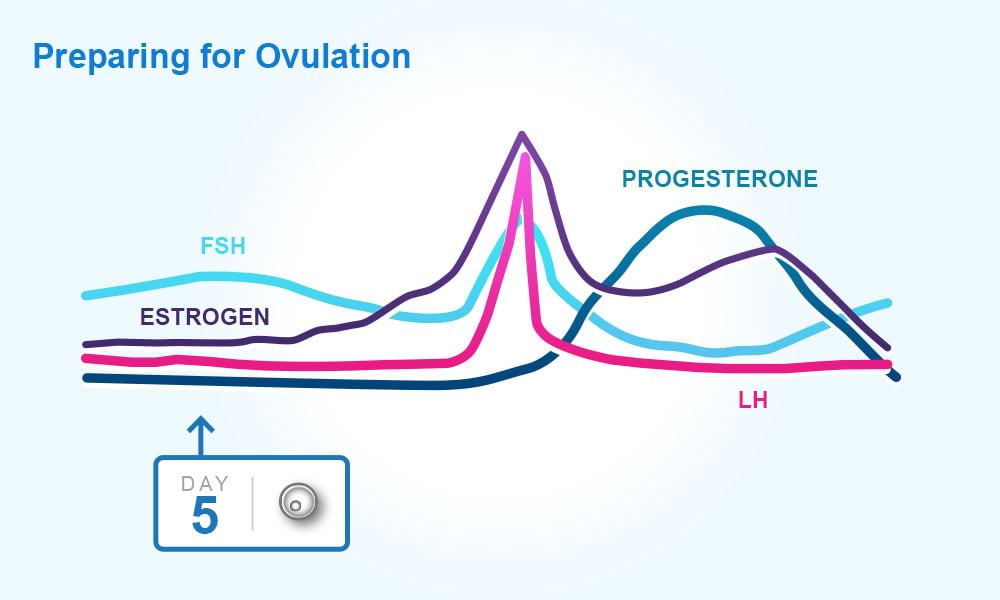
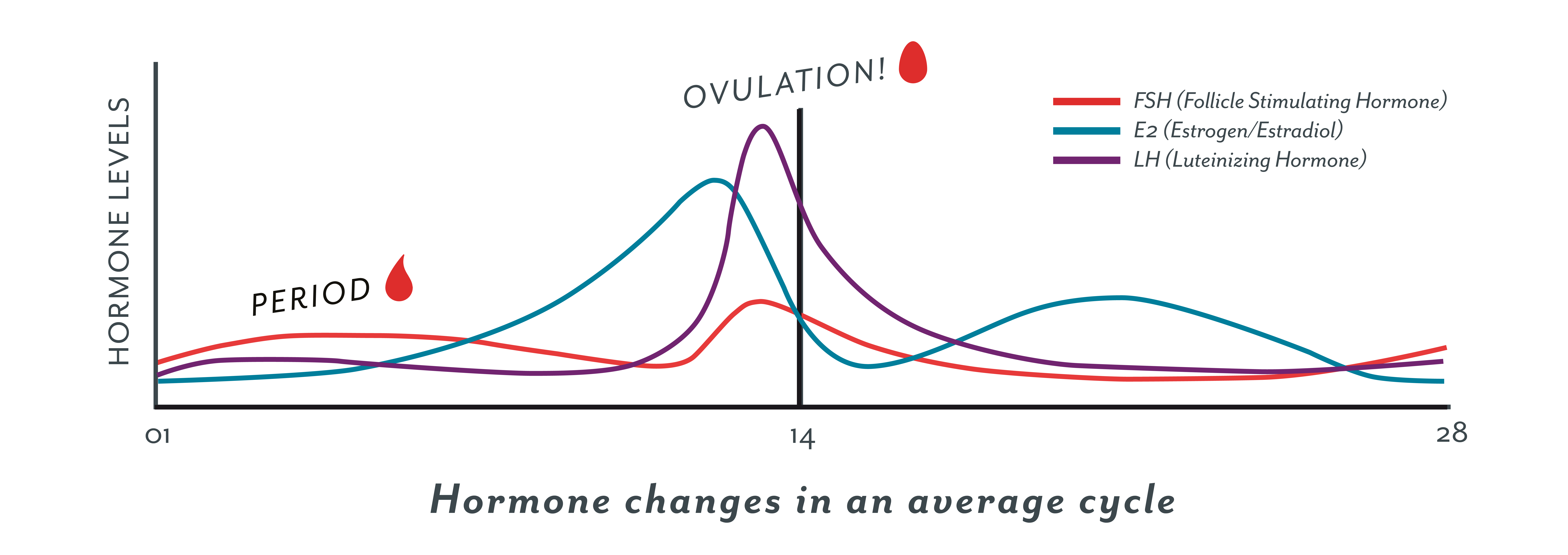
Hormone Changes After Ovulation

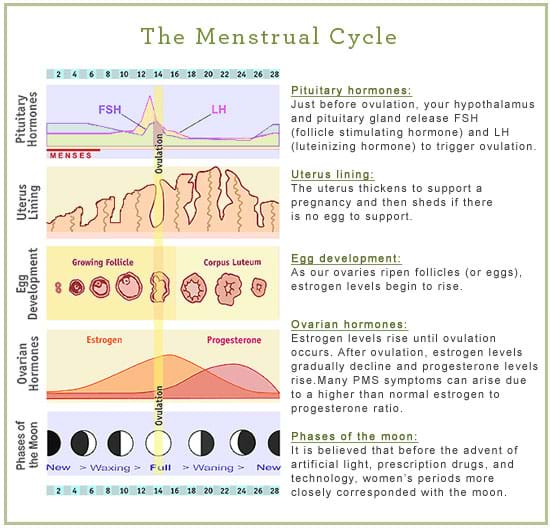
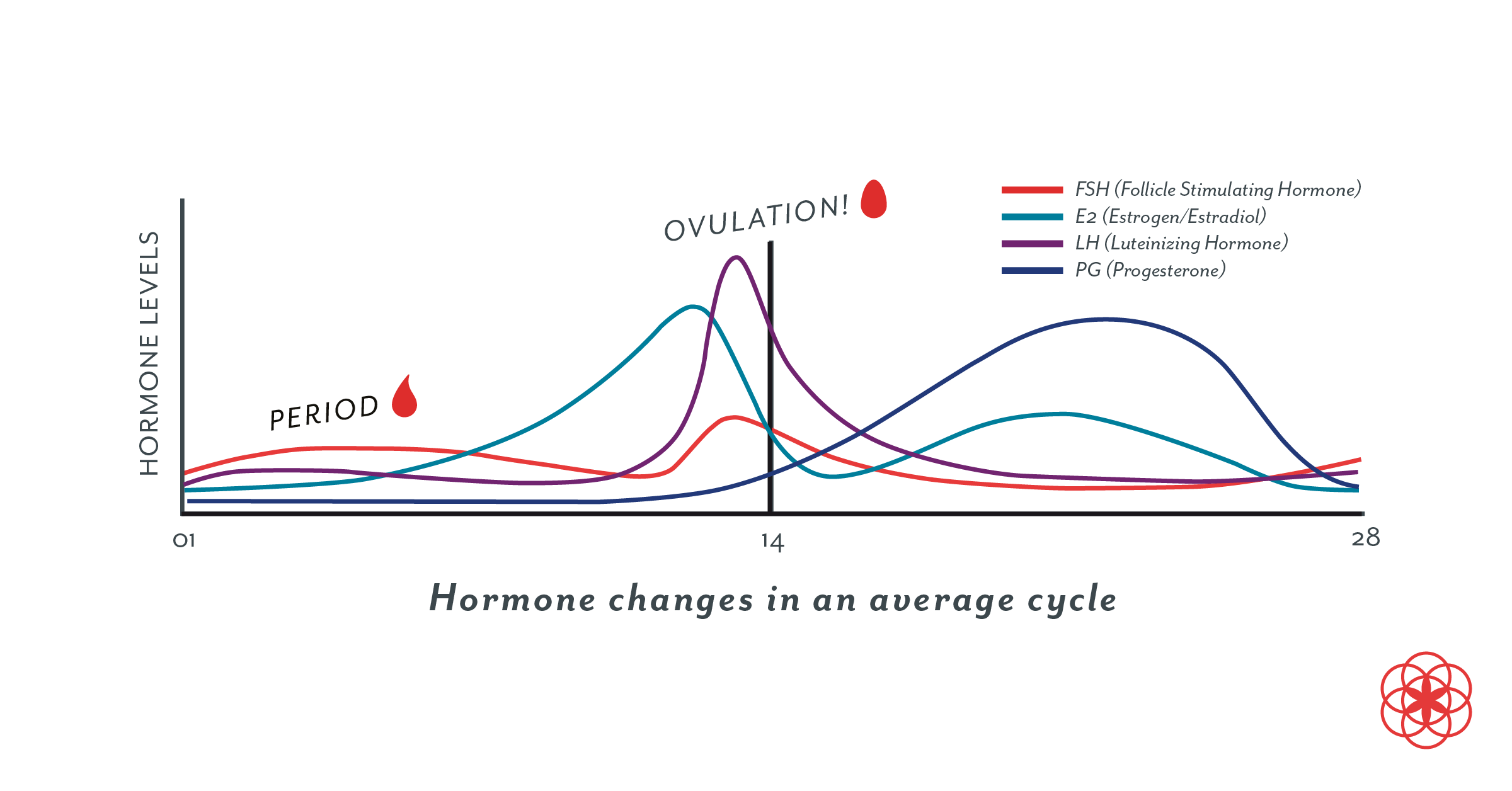
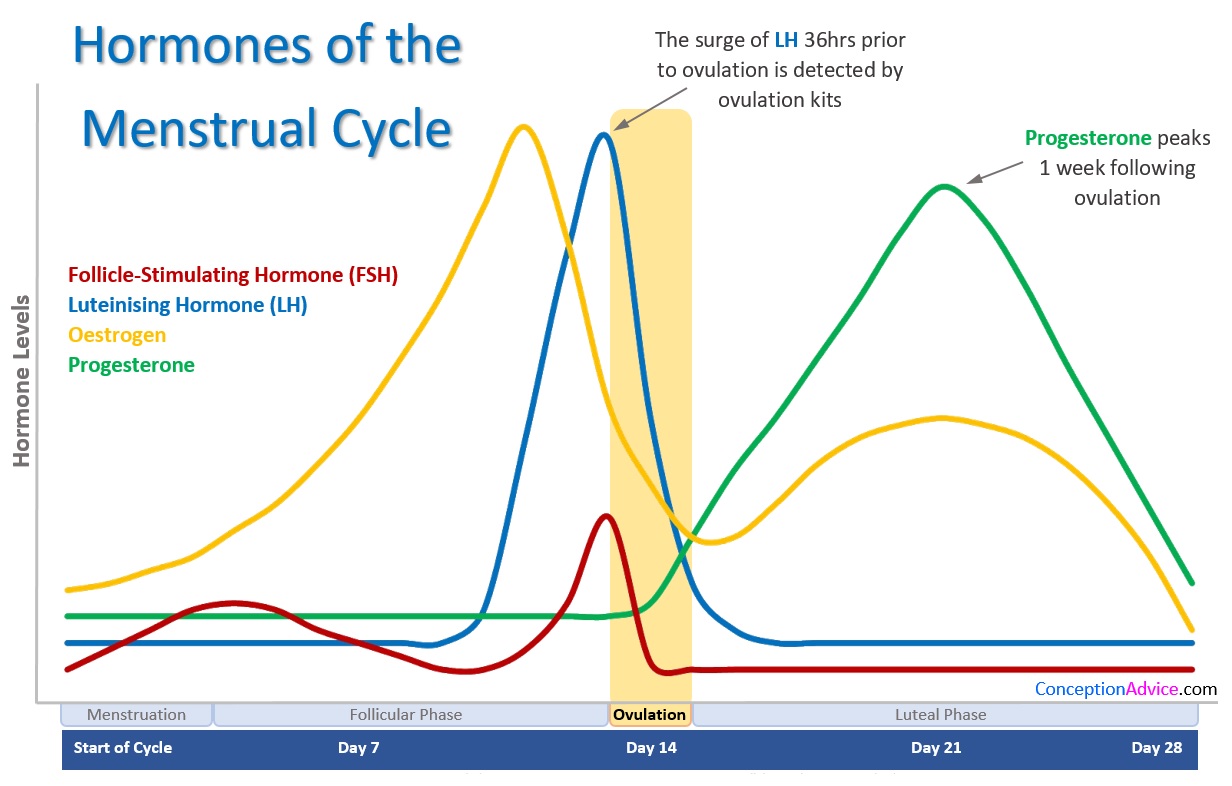
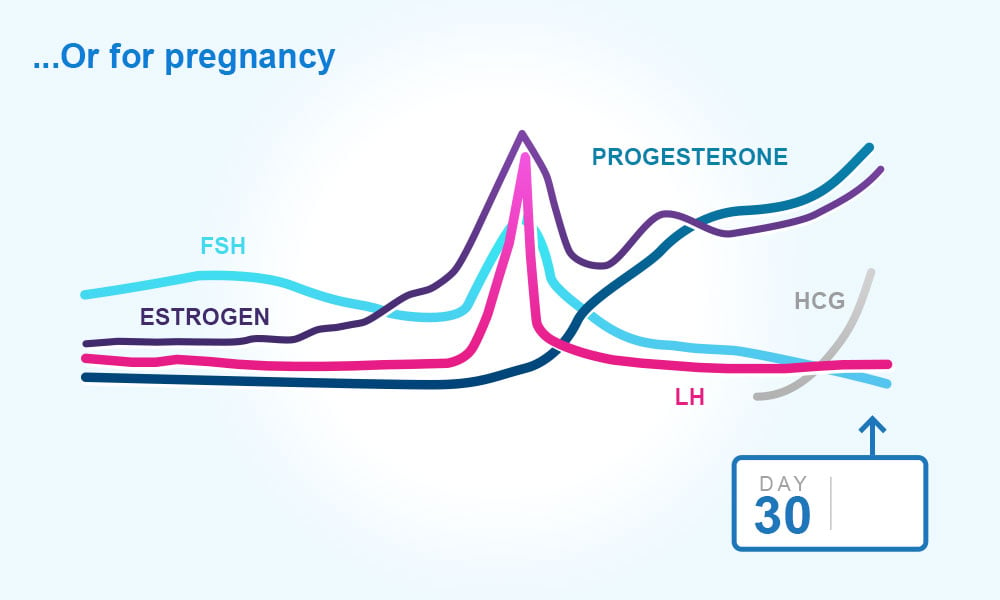
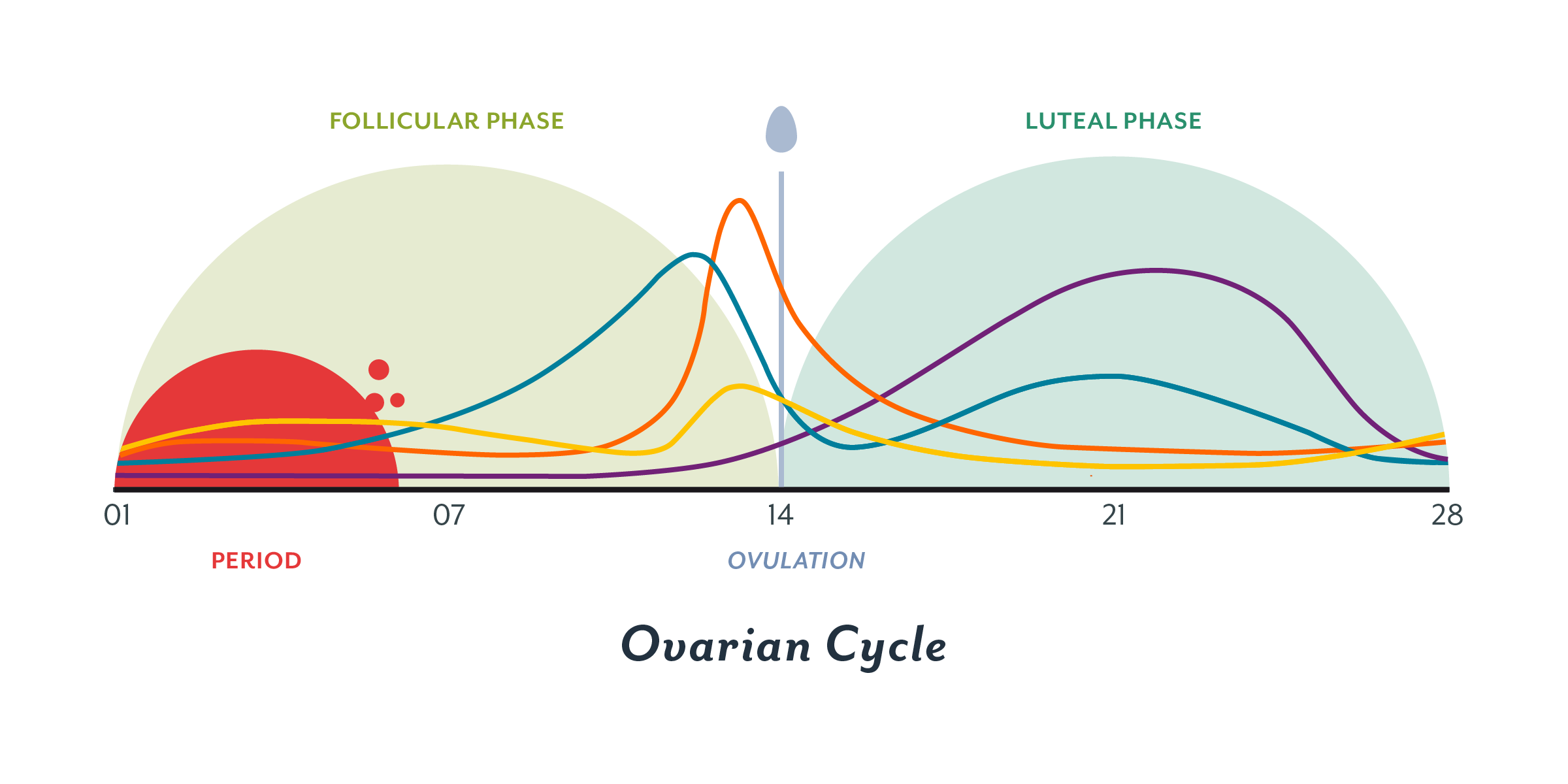
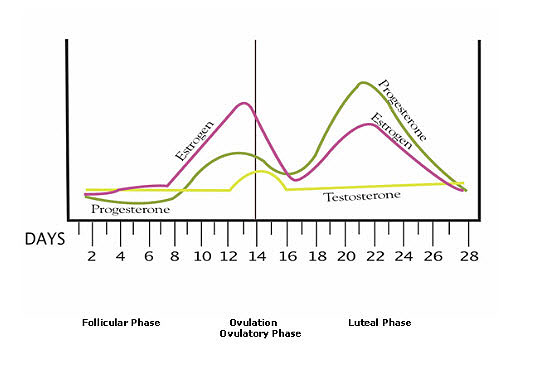
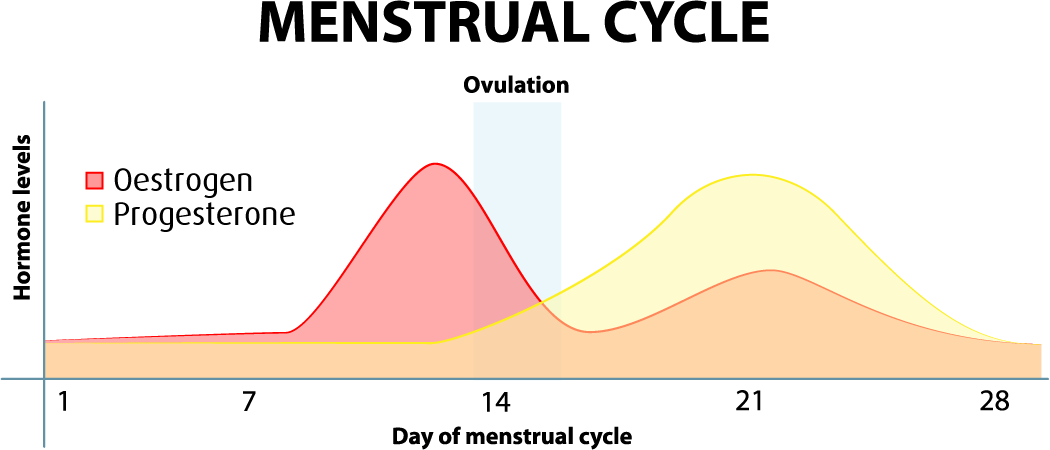
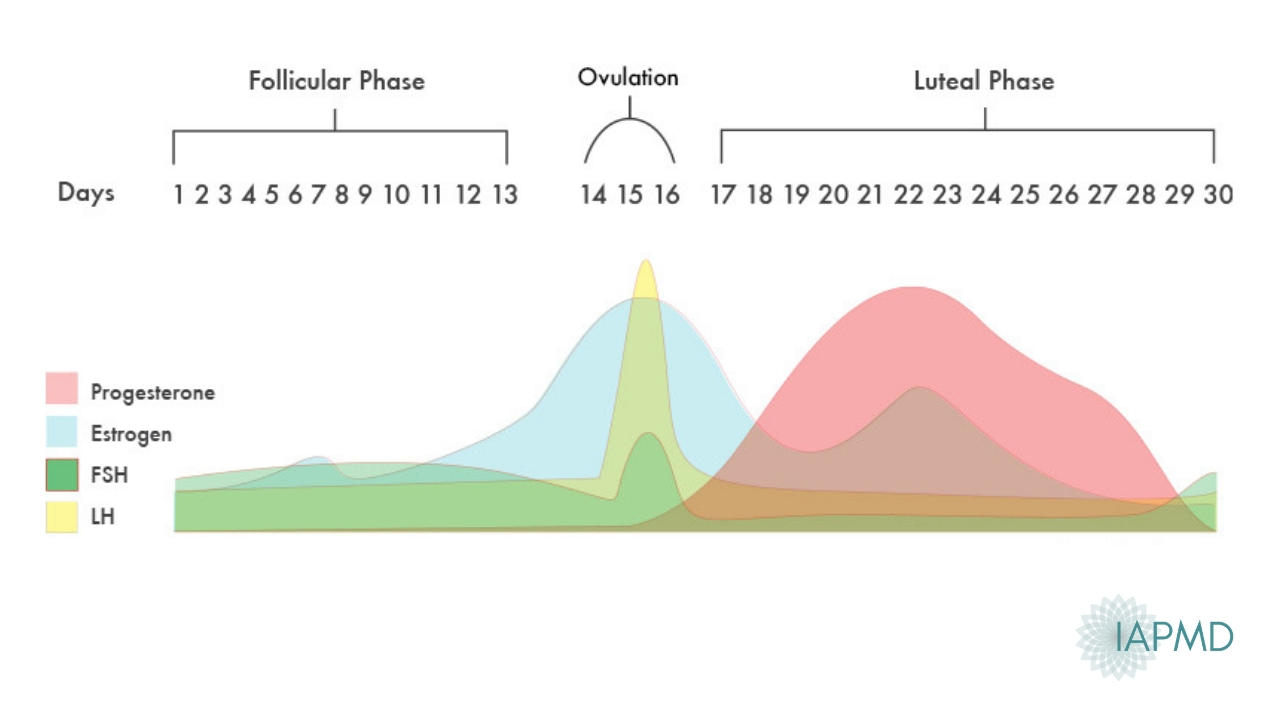
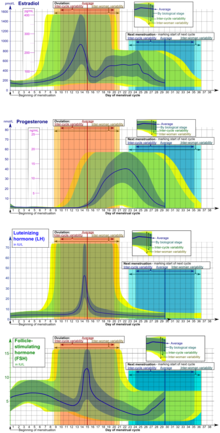
After the follicle releases its egg it changes into the corpus luteum this structure releases hormones mainly progesterone and some estrogen.
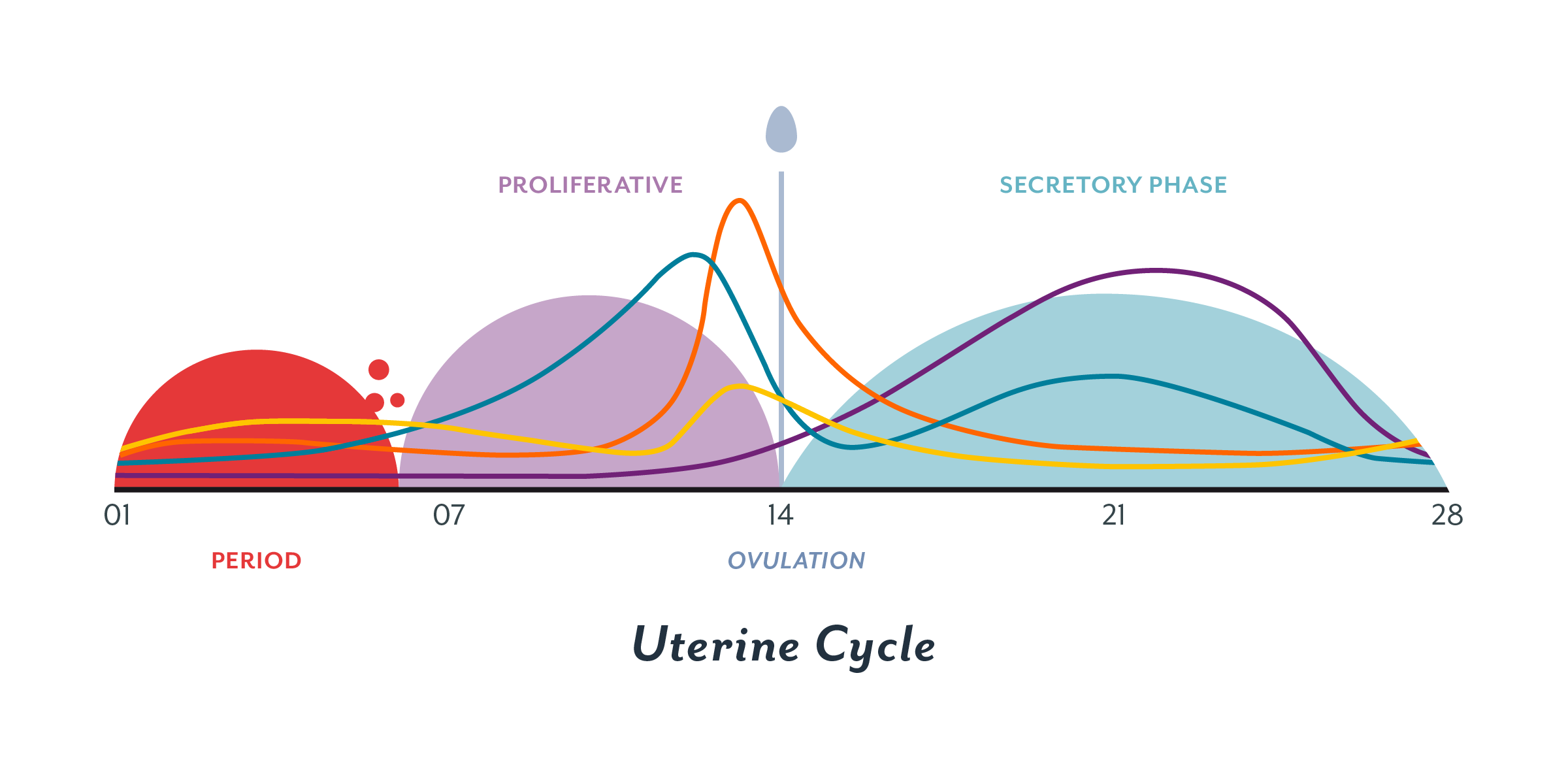
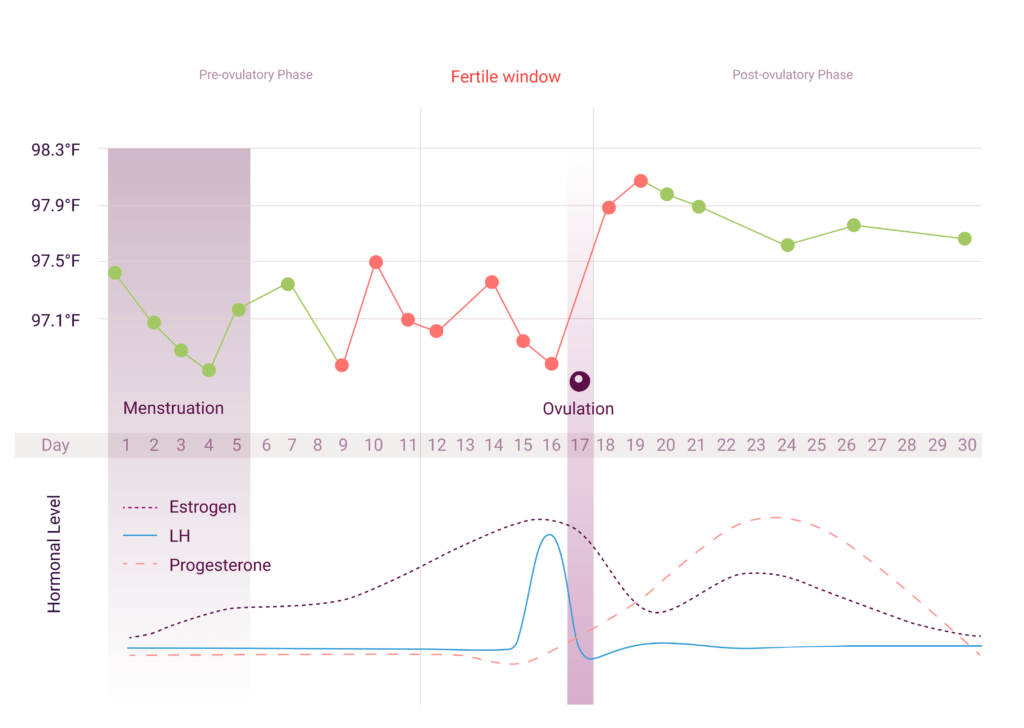
Hormone changes after ovulation. Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries in women this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. These thick walls are perfect for implantation of a fertilized egg. The estrogen level peaks approximately one day before ovulation in a 28 day cycle this is is typically day 13. Corpus luteum is left over in the fallopian tube.
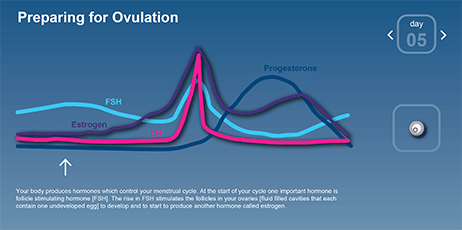
After ovulation during the luteal phase the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm in addition the uterine lining endometrium is thickened to be able to receive a fertilized egg if no conception occurs the uterine lining. The corpus luteum signals a progesterone increase which leads to a thickening of uterine walls. As the follicle develops and matures it produces the hormone estrogen. The rise in hormones keeps your uterine lining thick.
What tracking each of these hormones can tell you. Lower e2 relative to the days before ovulation brings about changes in cervical mucus and progesterone leads to a detectable increase in basal body temperature. There are two main hormone driven physiological changes you might notice after ovulation. After about 10 days the estrogen levels reach high numbers.
Ovulation leads to a corpus luteum a hormone secreting structure which produces elevated amounts of progesterone. During the ovulation phase luteinizing hormone lh surges from the pituitary gland triggering ovulation about 24 to 36 hours later. This is the phase where you can get pregnant. Ovulation is generally regular without any extra symptoms aside from changes in vaginal secretion cervical mucus increases in quantity and becomes clear and stretchy like egg whites during this phase.
Different types of vaginal discharge occur throughout the cycle so discharge that slightly changes color and consistency may be normal. Read on to learn more. This prevents unopposed estrogen or an imbalance of high estrogen she says. While some hormone levels fluctuate throughout your lifetime and may just be the result of natural aging other changes occur when your endocrine glands get the recipe wrong.





















/what-is-egg-white-cervical-mucus-ewcm-1960232-5b97ea3546e0fb00251d46df.png)