Ovulation And Hormones Involved

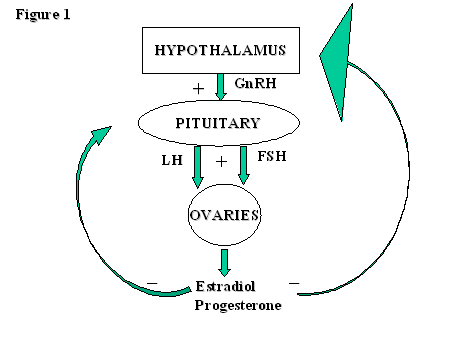
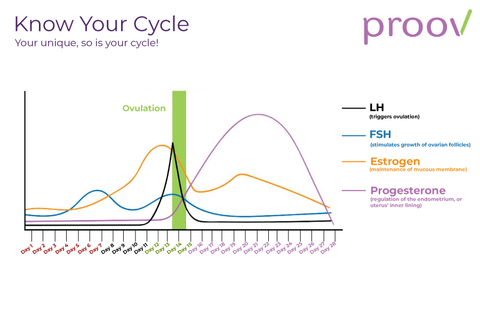
Functioning of this axis is dependent on the correct synchronization of the timing of release and the quantity of the hormones involved.
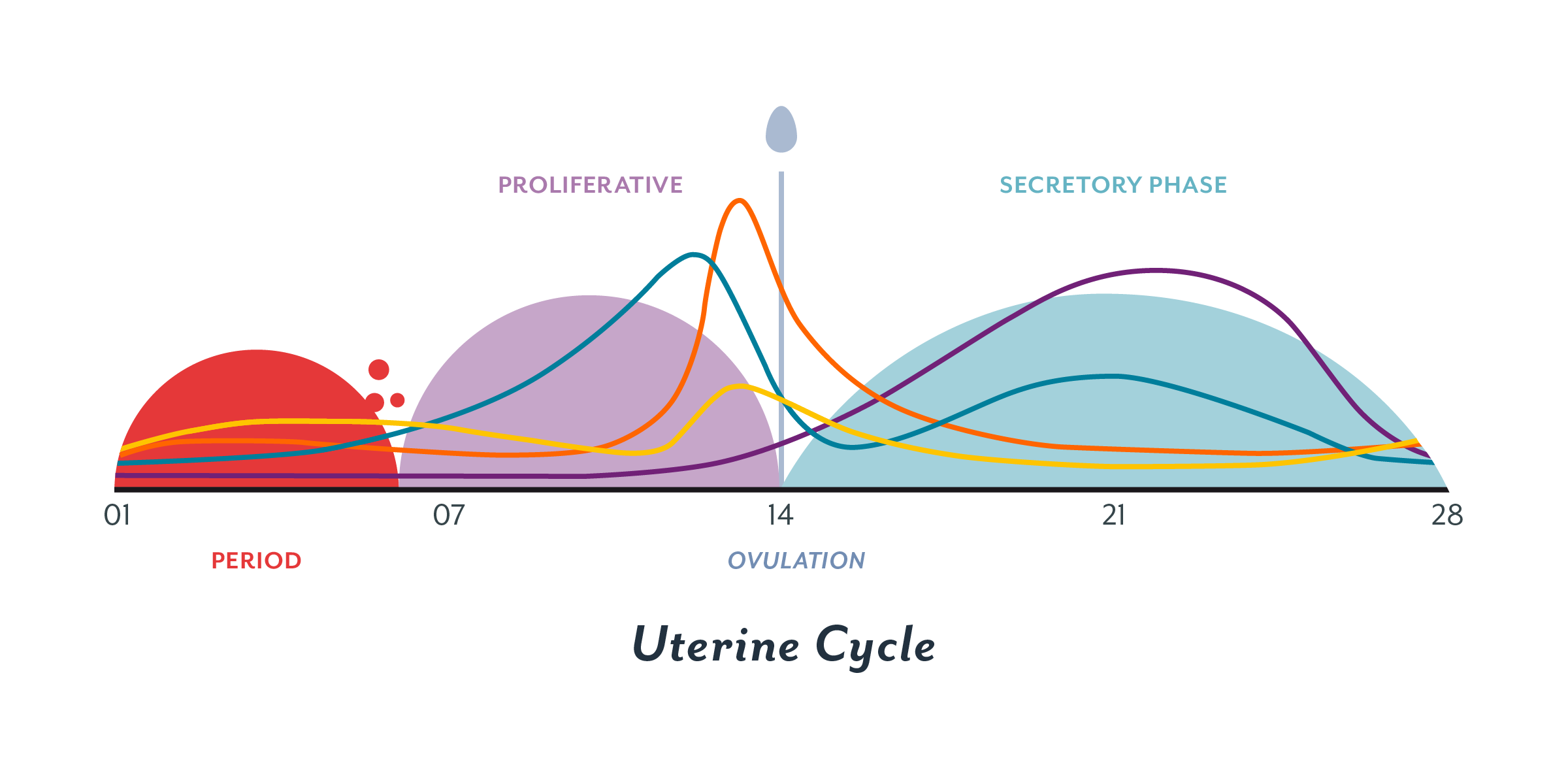
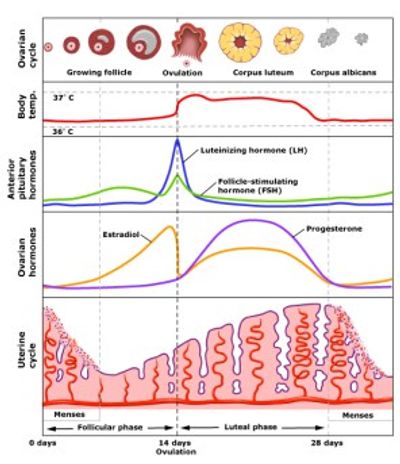
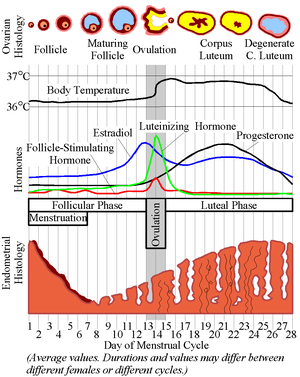
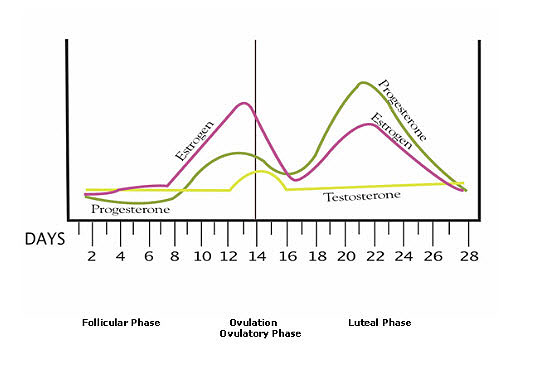
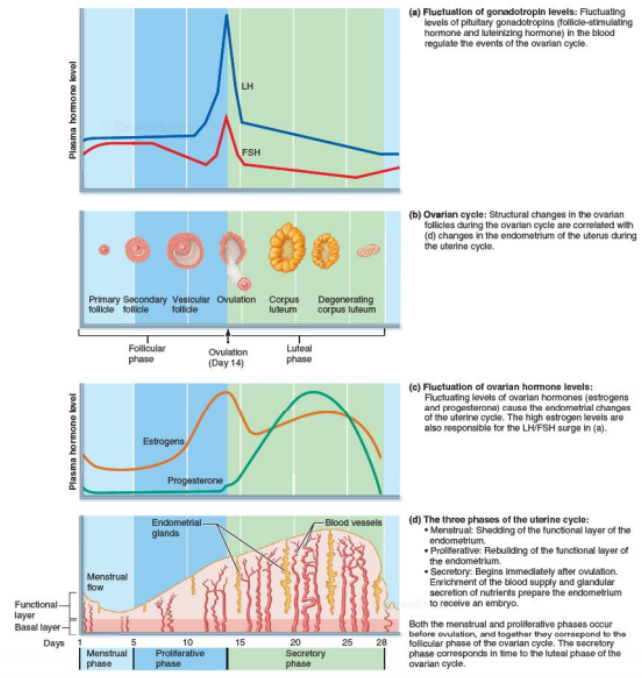
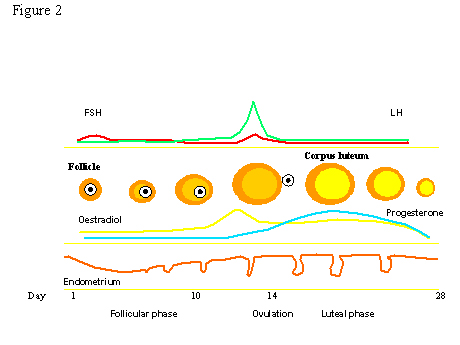
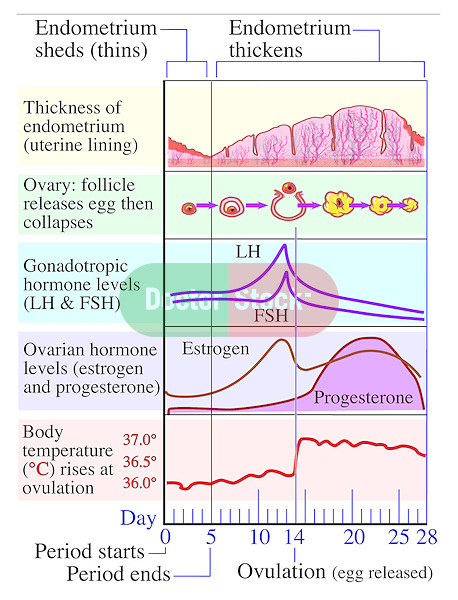
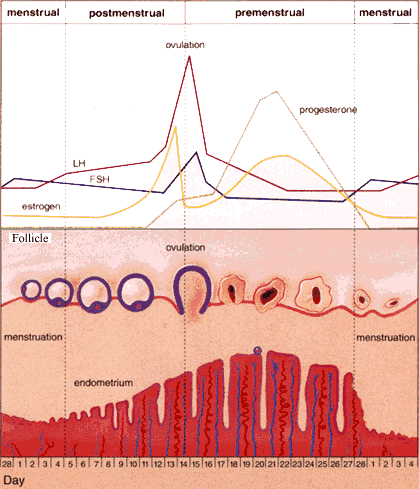
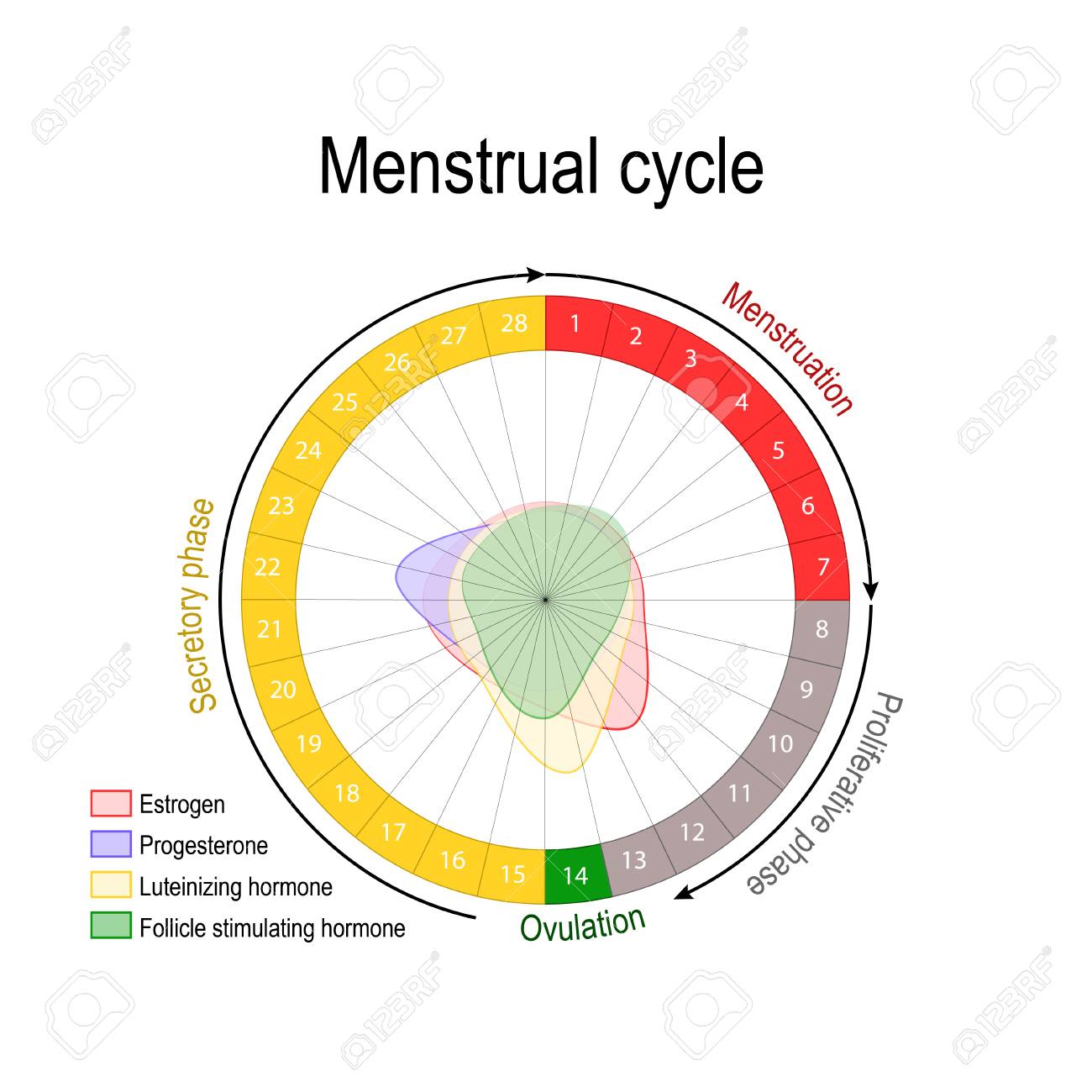
Ovulation and hormones involved. After ovulation during the luteal phase the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm in addition the uterine lining endometrium is thickened to be able to receive a fertilized egg if no conception occurs the uterine lining. After a day the egg will die or dissolve if it isn t. Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries in women this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. Once the cycle has gone through the ovulation begins as the egg is released from its follicle.
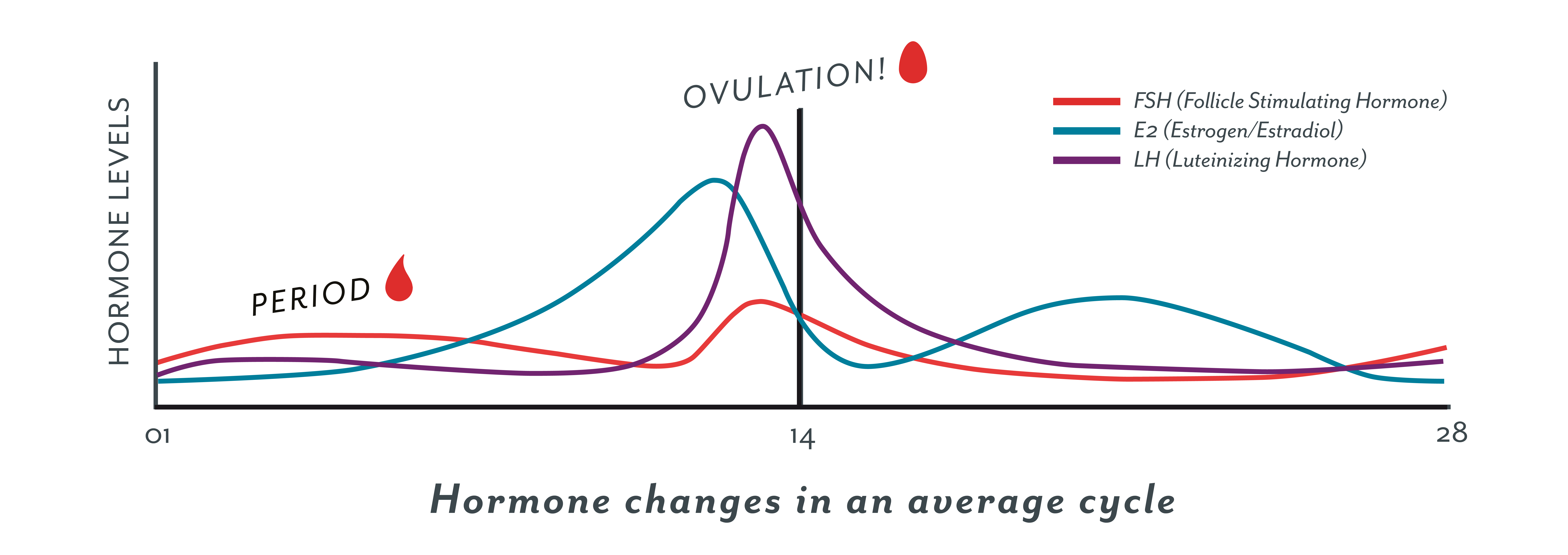
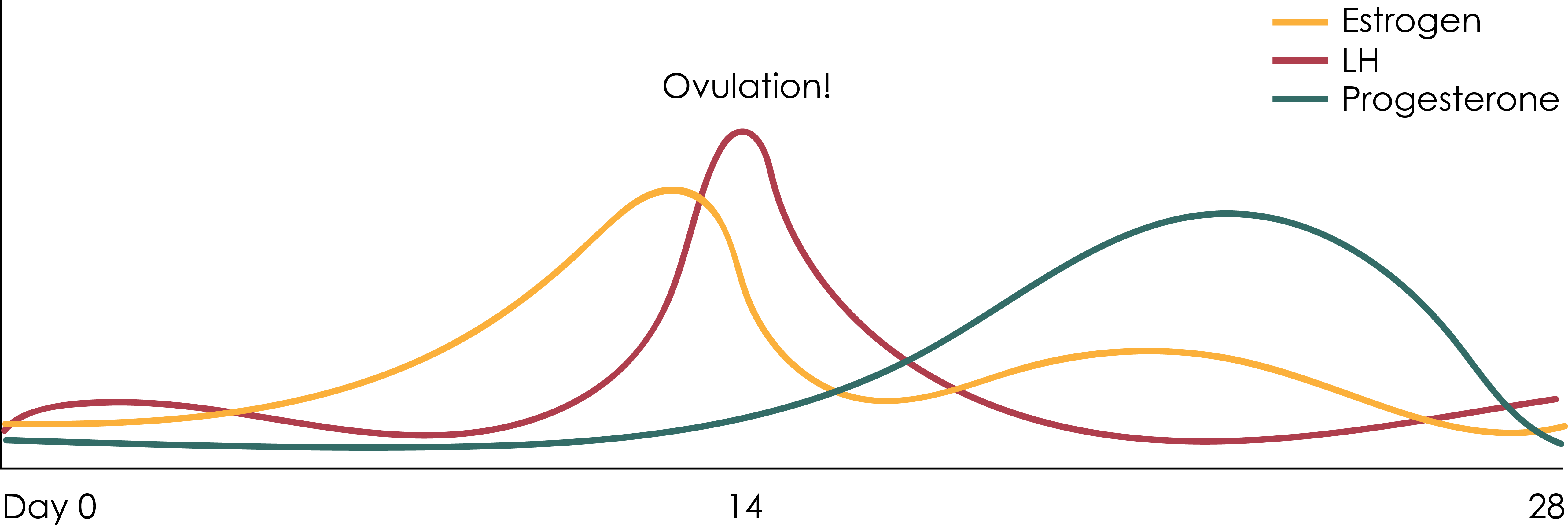
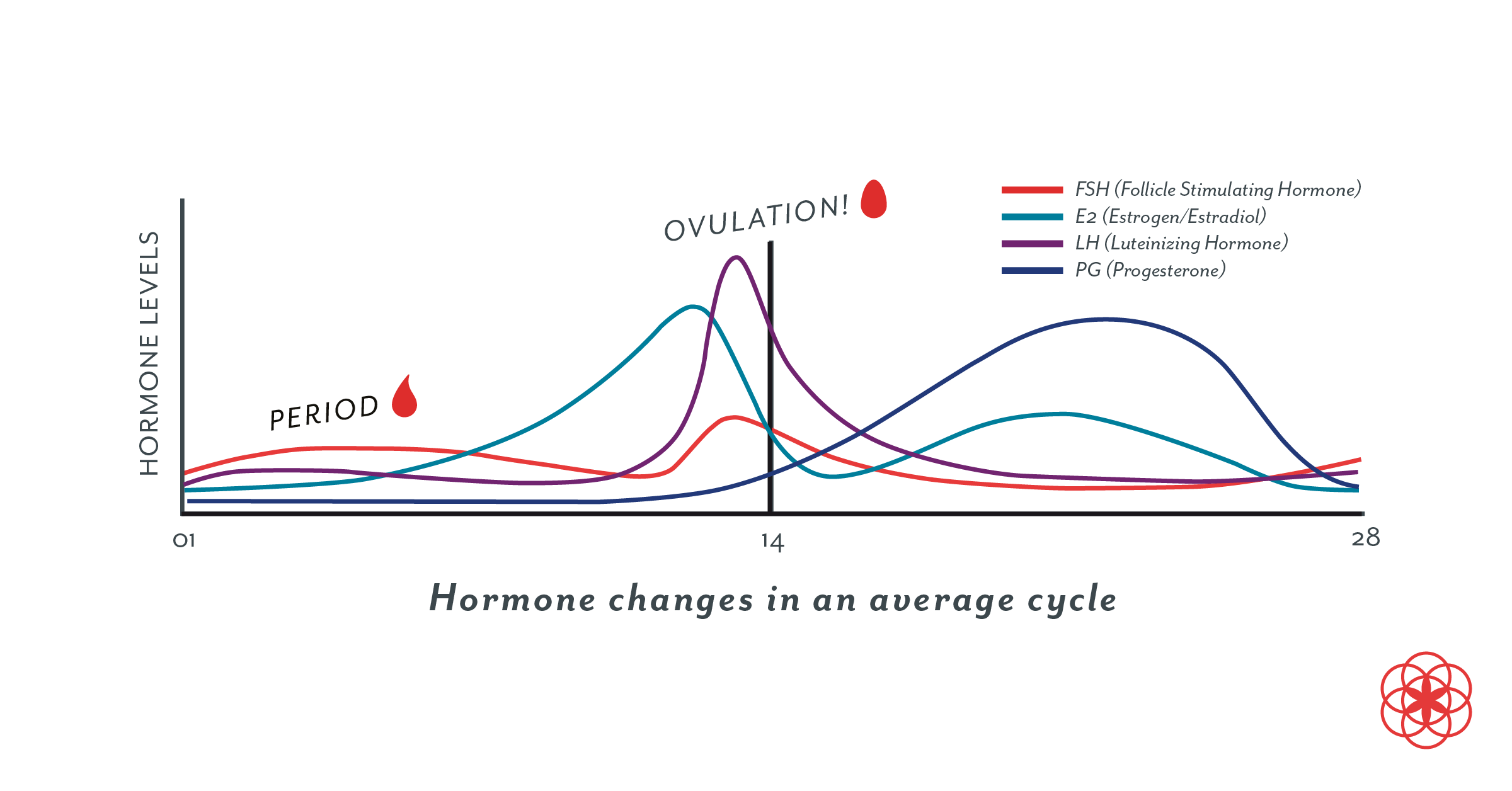
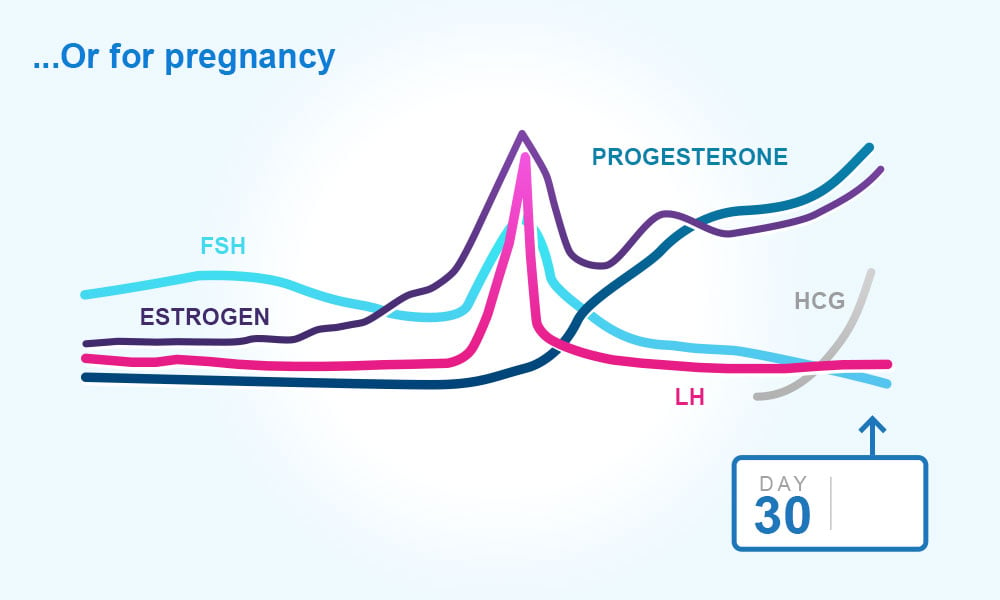
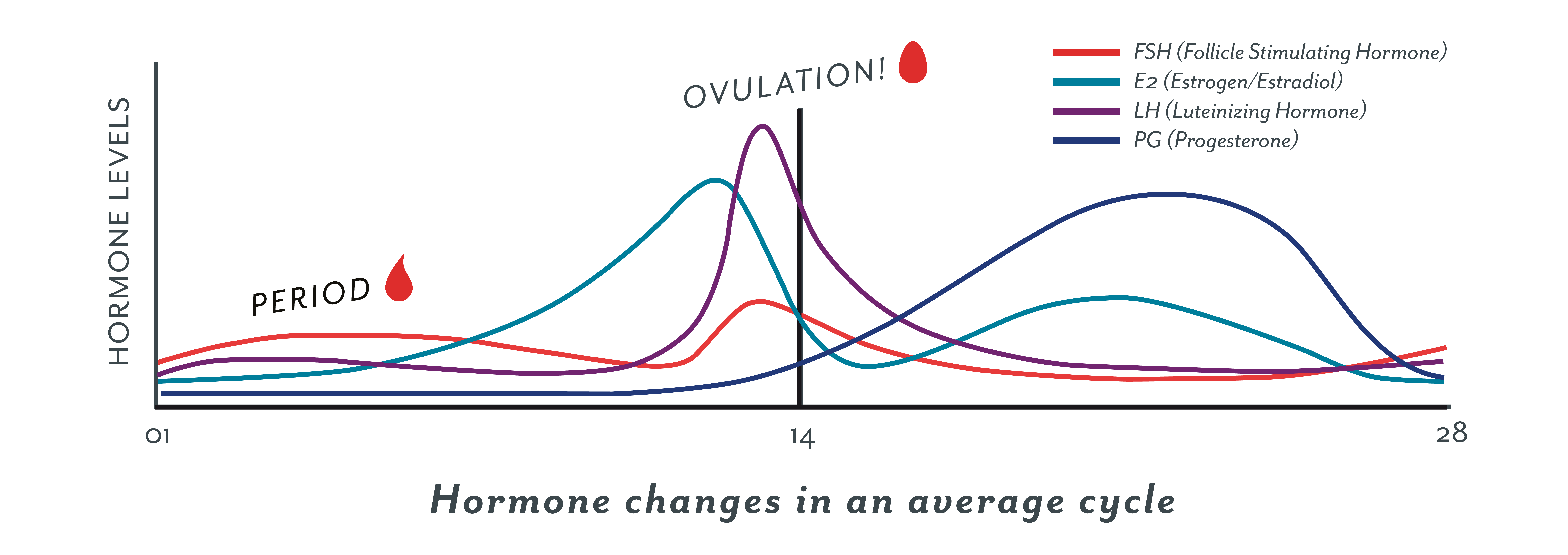
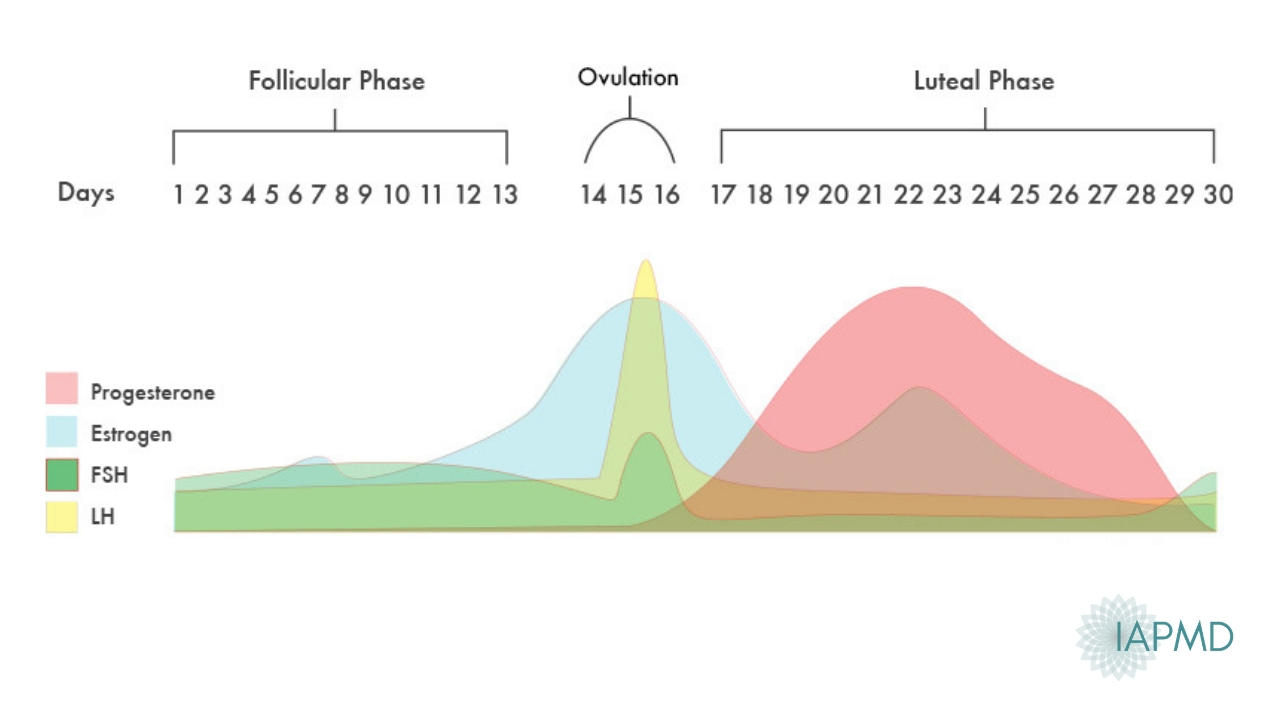
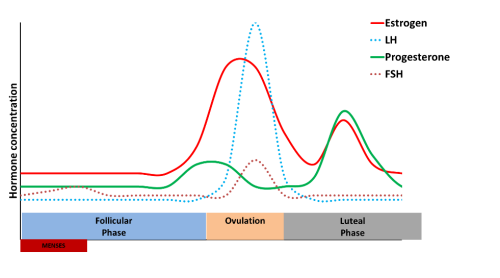
Estimation of the urinary output by chemical methods gives an indication of the blood levels and of the total production of these substances. In the normal course of events ovulation occurs once a month between the time of menarche and menopause. All the hormones involved in the hypothalamic pituitary ovarian axis rise in one period of the menstrual cycle and drop in the other. If after ovulation the egg is not fertilized the corpus luteum will begin to shrink.
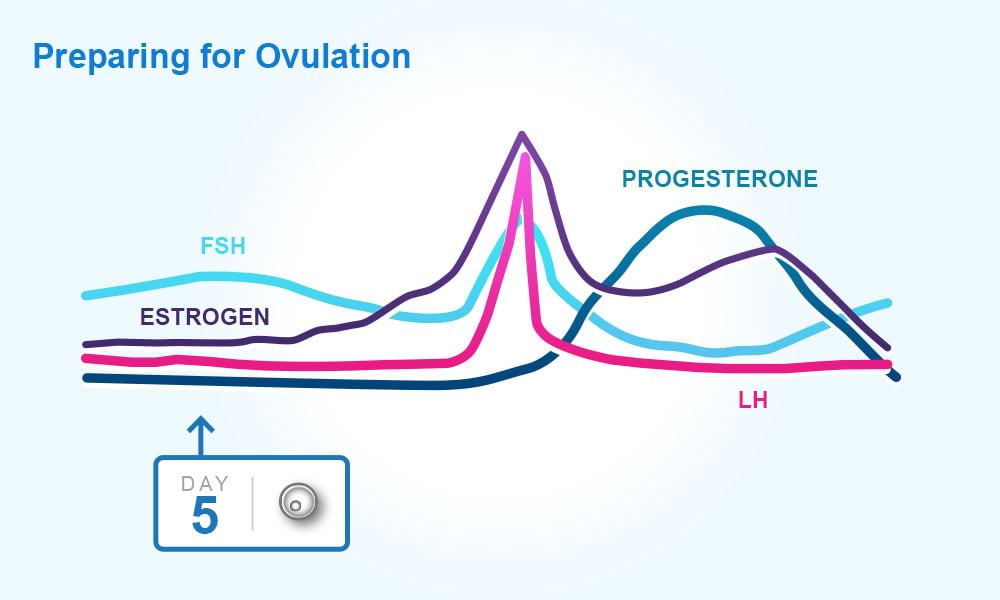
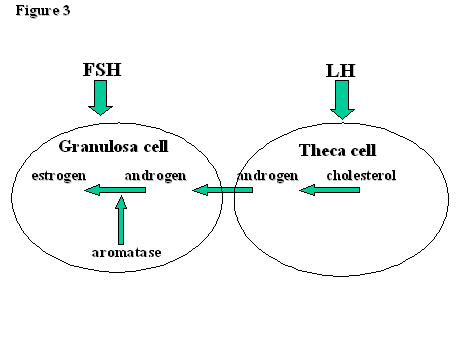
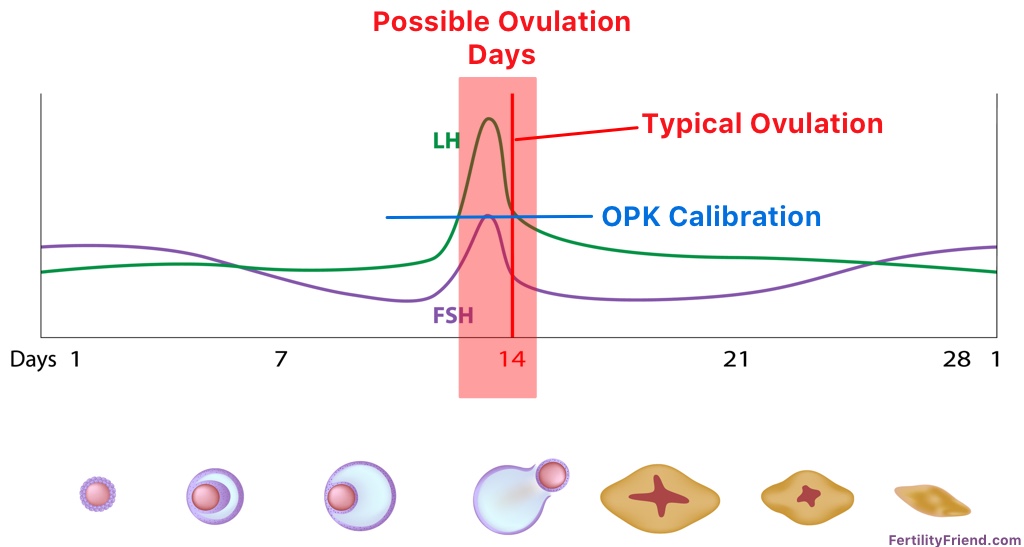
Ovulation happens at around day 14 if you have a 28 day cycle right in the middle of your menstrual cycle. The gonadotrophin releasing hormone gnrh follicle stimulating hormone fsh. The pituitary hormones fsh and lh help the egg sac or follicle grow and mature. The ovarian hormones circulate in the blood and are excreted in modified forms in the urine.
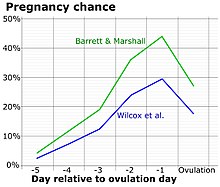
You may feel symptoms like fatigue. If the egg is fertilized the hormones begin to even out or increase depending on their need for the gestation process and. The term ovulation refers to the release of a viable oocyte from the ovary. It lasts about 24 hours.
All of these fluctuations affect ovulation and can cause symptoms like acne negative mood headache weight gain bloating and appetite changes. Hormones are a crucial part of your overall health. There are several natural estrogens and numerous synthetic modifications of these and of. The hormones released during the ovulation cycle act as both big and small activators to the ovulation and conception process.
A sudden surge of lh induces ovulation the ovary produces estradiol to prepare the pelvic organs and progesterone after ovulation to stabilize the endometrial lining for pregnancy. During your cycle your body produces five different hormones. The graph below shows the hormones that are involved in ovulation and how they must change throughout the cycle in order for ovulation to occur. The lining will begin to shed off.
It stops making progesterone which leads to no more hormones being made to support the uterine lining. Menstruation menstruation hormonal control of menstrual cycle.